Melting iron scrap and molding into various desirable shapes to be used later. It needs high heat to be applied in order to melt. There are many different ways through which iron could be mold; the two basic ways of melting iron scrap are by applying heat or by applying electricity. Application of heat has been known for years but application of electricity for melting iron scrap was known half way through the nineteenth century. The furnace which uses electricity in order to melt iron scrap is known as induction melting furnace whereas the method which uses electricity for the process is called induction method. You may be wondering to know about an induction furnace and how it works. Read below to know more about it.
What is an induction melting furnace
An induction melting furnace is an electrical furnace in which metal gets molten by applying high power or electricity. It is capable of handling a metal in various amounts ranging from less than a kilogram to hundreds of tons. It is capable of melting different precious metals like copper, iron, aluminum and steel. It is said to be far better in performance than heating furnace due to its efficiency and capability of handling different amounts of melting iron scrap. You may be interested to know the advantages of induction melting furnace over heating furnace.
Advantages of induction melting furnace
It makes use of energy efficiently
It avoids loss of extra energy as a specific electrical current is provided according to the amount of metal to be molten
It is well controllable
Cost effective
Cleaner melting
Compact installation
Natural stirring
It does not emit dust
Low metal loss
It does not give off harmful pollutants in the air
High power efficiency
Higher yield
Due to the above mentioned reasons, cupolas are now being replaced by induction furnaces as they melt iron without giving off harmful pollutants and makes no loss of valuable alloying elements.
Principle of induction melting
The principle upon which induction melting furnace works is that a high electrical voltage from a primary coil or source induces a low voltage and high current in the secondary coil or metal. Thus, induction furnace is ideal for melting different kinds of metals and making alloys of them with no or minimum metal losses. This makes little refining of metals possible but metals cannot be highly refined through it. This is a big drawback in induction refining besides having many advantages.
Types of induction melting furnaces
There are two main types of induction melting furnaces
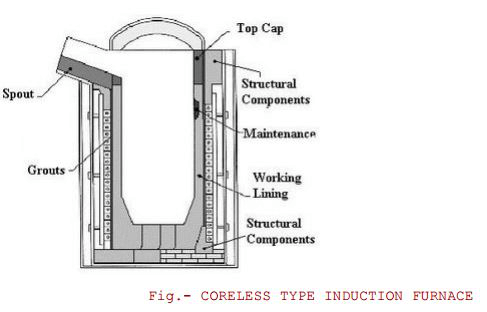
1. Coreless induction furnaces
The main and most important part of coreless induction furnaces for melting iron scrap, which is said to be its heart is a coil consisting of a hollow tubing made of copper. It is a heavy duty and highly conductive tubing which is wound onto a helical coil which is contained in a steel shell further coated in magnetic shielding which prevents the steel shell from being heated. Further, in order to protect the shell from being over heated, the coil is circulated in a cooling tower.
The interaction between magnetic field and electric field is produced when the charge metal is molten. It produces a stirring action which lets the metal rise upwards in the center. The degree of stirring depends upon the power and frequency being applied and as well as the size and density and viscosity of the molten metal. This stirring action is of great importance as it helps mixing of alloys and the temperature throughout the furnace becomes homogenous.
Crucible furnaces are used instead of coreless induction melting furnace for melting alloys who have a high melting point. Whereas coreless furnace can be used for melting all kinds of steels and iron. Moreover, coreless furnace is found to be ideal for alloying because of its high degree of control over temperature. The below figure shows the structure of coreless induction furnace:
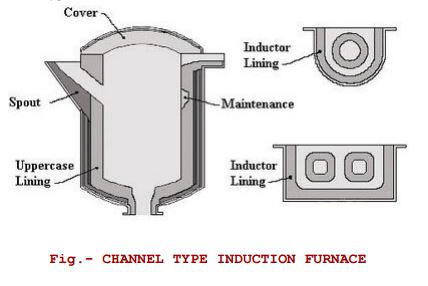
2. Channel induction furnaces
Channel induction melting furnace consists of a refractory lined steel shell containing the molten metal. The induction unit forms the melting component of the furnace and is attached to the steel shell. The primary induction coil is wound around a ring made by iron core. This structure looks like a transformer in which secondary coils are comprised of molten metal loops. The metal is circulated into the furnace due to the heat being generated within the loops. This circulation of molten action produces a stirring action in the furnace.
The stirring action is responsible for completely mixing the molten metals to form alloys. It is basically used for melting alloys having low melting points. These furnaces are used as metal holders for keeping the metal enough hot to not to demand very high temperature at peak.
Heated furnaces demand high fuel at peaks for melting, especially for alloys and metals whose melting points are high. Therefore induction melting furnace is said to be the better, satisfactory and clean method for melting iron scraps. The following figure shows the structure of channel induction furnace:

 © Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited
© Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited