Mini Laser Welding Machine
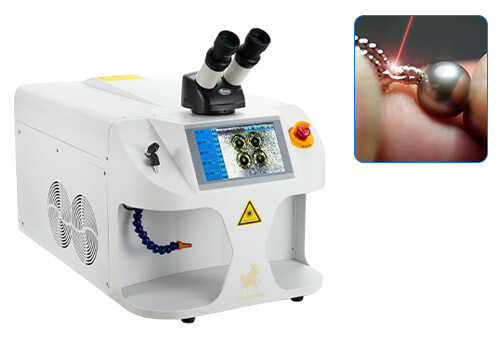

The mini laser welding machine is a compact size jewelry welding machine that is used to weld noble metals together in the jewelry making industry.
The mini laser welder uses an amplified beam of light to produce a solid weld with an invisible spot within seconds. The beam of light emitted from a jewelry laser welder is concentrated, adjusted and controlled by the user.
When adding metal or repairing jewelry using the jewelry welding machine, the same noble alloy is welded. The heat used in the welding process is localized such that the result of welding is seamless or result in no discolouration of the welded spot.
Superbmelt jewelry laser welder for sale is able to weld base metals, karat gold, sterling silver, palladium, platinum, etc.
The mini laser welder allows you to weld continuously while holding precious metal pieces in your hand. Laser welding when compared to soldering is faster, neater and more cost effective for many manufacturing and repair purposes.
| Model | SPB-150WB |
| Wavelength | 1064nm |
| Max output power | 150W |
| Max pulse energy | 80J |
| Pump source | Single lamp |
| Pulse width | 0.1-20ms |
| Pulse frequency | ≤50Hz |
| Aiming and positioning | Microscope + camera system |
| Application | Welding and repairing various precious metal trinkets |
| Host power consumption | ≤5KW |
| Electricity demand | AC220V±5%/50Hz |
| Cooling system | Water cooling + air cooling |
| Dimension | 660x385x435mm |
| Weight | 49kg |
- Superbmelt jewelry welding machine offers a high level of welding accuracy and control. The mini laser welder is so precise and allows you to weld the smallest parts without error or damages.
- The mini laser welder is capable of welding complicated joints. The jewelry laser welding machine allows you to weld dissimilar materials as well as complex areas that would be too difficult to reach using traditional welding methods.
- The mini laser welder requires low heat (only ≤5KW), reducing the distortion of components. Therefore, making the jewelry laser welder a preferred option in welding and repairing precious metals.
- With Superbmelt mini laser welder, you can make repeated and constant weld of jewelries. It is a faster welding technique than other traditional techniques.
- The mini laser welder allows jewelry manufacturers to make high strength welds. There is no need for filler materials to be used during welding. Laser welders provide excellent weld quality and clean processing, which makes it adoptable for use in the medical industry.
- Superbmelt jewelry laser welder makes use of both water cooling and air cooling as the cooling system, which contributes to the welding efficiency of the mini laser machine.
- The mini laser welder is compact size, easy to move and use, this is why it is adopted by the jewelry, medical, electronics, and automotive industries.
- The mini laser welder has an imported ceramic condenser cavity that is both corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance. This welder machine condenser has a lifespan of 8 to 10 years.
- The mini laser welder allows you to aim and position metal parts through a microscope and camera system.

2 years warranty
The warranty for our machine is one year longer than the warranty provided by other factories.

ISO CE SGS approved
Professional certification bodies certify that the machines are of high quality.

Strong service team
We will give response within 24 hours against your problem by our professional engineer.
Why SuperbMelt Mini Laser Welder



Any Question About SuperbMelt Mini Laser Welding Machine
1. Is laser welding as strong as MIG?
There are two distinct welding procedures, laser welding and MIG (metal inert gas) welding, and there are a number of variables that can affect how strong each is. This is a contrast:
Strength of Joints:
High joint strength may be achieved using laser welding, which is frequently on par with or even stronger than MIG welding.
MIG Welding: MIG welding, especially in structural welding applications, also yields robust joints.
Zone Affected by Heat (HAZ):
Laser Welding: The heat-affected zone is usually smaller with laser welding, which lowers the possibility of material deformation while preserving material strength.
MIG Welding: The strength of the material in the impacted zone may be impacted by the increased HAZ that results from MIG welding.
Control and Accuracy:
Laser Welding: Laser welding provides extremely high levels of control and accuracy, enabling intricate and precise operations. This may be useful in applications where complex welds are necessary.
MIG Welding: Although MIG welding is more adaptable than laser welding, it could not be as precise.
Compatibility of Materials:
Metals and alloys may be welded together using laser welding, among other materials.
MIG Welding: Despite its versatility, MIG welding may be limited depending on the kind of material.
Pace and Effectiveness:
Laser Welding: The efficiency of laser welding is boosted since it is frequently faster.
MIG Welding: While MIG welding is effective, its processing time may be somewhat slower than that of laser welding.
2. Do you need gas for laser welding?
No, unlike certain other welding techniques like MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, laser welding does not require the use of gas. A concentrated laser beam is used in laser welding to melt and fuse materials together. The laser’s energy is used in this procedure to heat the materials and fuse them together.
One benefit of laser welding is the lack of a shielding gas. In procedures such as MIG welding, shielding gases are frequently employed to shield the molten metal from ambient impurities like oxidation. There is less chance of air contamination with laser welding because it is a non-contact procedure and the heat source is a concentrated laser beam. Welds produced as a consequence may be more accurate and clean.
It is important to remember that laser welding does not eliminate the requirement for environmental considerations because there is no shielding gas involved. To guarantee the quality of the weld, the welding environment must be well controlled, and elements like atmospheric control and cleanliness may still be crucial.
3. How thick will a laser welder weld?
The kind and power of the laser, the material being welded, and the particular welding application are some of the variables that affect how thick a laser welder can successfully weld. In general, laser welding may be used to fuse a variety of materials, from thicker portions to thin foils.
Regarding laser welding thickness, keep the following things in mind generally:
High-Power Lasers: These lasers can fuse thicker materials together and can penetrate harder materials. In comparison to lower-power lasers, a laser with a larger wattage (e.g., 200W or 400W) can handle thicker metal portions.
Material Type: The absorption rates of laser energy and their thermal conductivities differ between materials. Lasers may be able to weld some materials more effectively than others, such as specific metals.
Beam Quality: The laser’s focus and energy concentration are influenced by the quality of its beam. A high-quality beam is useful for welding thinner materials because it provides fine control.
Welding Speed: The welding process may be affected by the laser’s speed as it passes through the material. When welding thicker materials, slower welding rates could be necessary.
Joint Design: The welding of thicker sections can be affected by the joint’s design and the welding arrangement (e.g., butt joint, lap joint).
It’s crucial to remember that, despite the versatility of laser welding, materials that are very thick can be better suited for other welding techniques like arc or electron beam welding.
It is advised to review the instructions provided by the equipment manufacturer and carry out testing to ascertain the ideal laser welder settings for particular applications and material thicknesses.
4. What is the greatest hazard to a welder while laser welding?
When laser welding, the biggest risks to a welder are laser radiation exposure, fumes, and potentially hazardous chemicals. The following are some major risks connected to laser welding:
Optical Radiation:
Eye Hazards: Direct or reflected laser radiation exposure might result in retinal damage among other eye ailments. Welders need to use laser safety goggles that are the right optical density for the particular laser wavelength.
Skin Hazards: Burns to the skin can result from prolonged exposure to high-power laser beams. Wearing protective gear and clothes is crucial to reducing skin exposure.
Gases and Fumes:
Hazardous Fumes: When dealing with specific metals or coatings, laser welding, among other welding processes, can emit fumes and gases. Breathing in these vapors may be hazardous. To reduce exposure, sufficient extraction or ventilation systems should be installed.
Material Risks:
Material Off-Gassing: When exposed to high temperatures, certain materials might emit dangerous gasses, which can happen during laser welding. It’s essential to understand the materials being welded and to take the proper safety precautions.
Energy-related Risks:
Electric Shock: Electrical components are used in laser welding equipment. Electric shock is a possibility, particularly while working with power supplies and high-voltage components. The right electrical safety precautions have to be taken.
Risks of Fire:
Material Ignition: Working with combustible materials can be particularly risky due to the elevated temperatures produced during laser welding. It is important to take fire safety precautions, such as clearing the work area of combustibles.
Engineering Dangers:
Robotic systems or moving parts may be present in certain laser welding devices. If appropriate safety procedures are not taken, there is a chance that moving parts will injure someone.
Welders should receive the necessary training, use personal protection equipment (PPE), adhere to the manufacturer’s safety instructions, and operate in well-ventilated settings in order to reduce these risks. Employers bear the responsibility of putting safety procedures into place and making the workplace safe for laser welding activities.
5. Are laser welders strong?
Yes, laser welders have a reputation for creating accurate and durable welds. The concentrated and focused energy produced by the laser beam is what gives laser welding its power.
Control and Accuracy:
High levels of accuracy and process control are made possible by laser welding. A precise guided focused laser beam may produce a clean, well-controlled weld at the welding site.
Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) Minimum:
The smallest heat-affected zone, or the area surrounding the weld where the base material is somewhat heated, is produced by laser welding. Lowering the heat-affected zone improves the weld strength and preserves the mechanical characteristics of the material.
Deep Dwelling:
Deep penetration welding is one of the laser welding techniques that enables the laser beam to pierce the material deeply, producing strong and long-lasting welds. For heavier fabrics, this is very beneficial.
Clear-cut and Accurate Fusion:
A precise and clean fusing of the joined materials is accomplished by the laser welding technique. The overall strength and integrity of the weld are enhanced as a result.
Content Flexibility:
Many materials may be joined with laser welding, including metals, alloys, and certain non-metallic materials. This adaptability enables the safe welding of many material kinds.
Decreased Distortion:
The welded materials have less distortion because to the laser welding process’s accuracy and control. Lower distortion adds to the weld’s improved overall strength and dimensional precision.
It’s important to remember that certain welding settings, the kind of laser being used, and the characteristics of the materials being welded all affect how strong a laser weld is.
6. Is laser welding as strong as arc welding?
The strength of laser welding, which is renowned for producing accurate and durable welds, varies depending on a number of variables, including particular applications, welding conditions, and material properties. Because laser welding is so precise, it’s perfect for complex and elaborate work. By creating a small heat-affected zone (HAZ), it lowers the possibility of material deformation while preserving mechanical qualities. Additionally, the fusing of materials produced by laser welding is exact and clean.
However, arc welding offers advantages due to its adaptability and suitability for a range of materials and thicknesses. Deep penetration may be achieved with certain arc welding techniques, such as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). Arc welding techniques could be more economical in some circumstances for particular uses.
The decision between arc and laser welding ultimately comes down to the particular needs of the welding job. When used properly, both techniques may yield strong welds and have their benefits.



 © Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited
© Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited