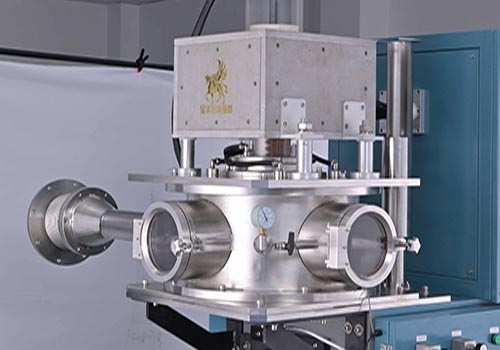
Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine
SuperbMelt vacuum continuous casting machine assists customers in casting high-quality jewelry plates or tubes.


SuperbMelt Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine utilizes its high vacuum pressure to cast high-quality, smooth, and pore-free raw materials for gold, silver, copper, K gold, and other metal jewelry, including sheets, tubes, and rods.
The Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine comes with stirring function, inert gas protection, and vacuum secondary feeding capabilities to prevent metal oxidation, ensuring uniform color in the finished products. This machine can cast 2kg of metal raw material in a single operation and is suitable for jewelry production, semiconductor manufacturing, solder production, and other industries.
- Industry: Jewelry Casting, Precious Metal Processing, University Laboratories, and related fields.
- Metals: Gold, K Gold, Silver, Copper, and their alloys.
| Model number | SPB-HVLS | SPB-HLS |
| Power source | 380V | Single phase 220V, 50/60Hz |
| Power | 15 kw | 15kw |
| Applicable metal | Gold, Silver, Copper, Brass, Bronze, and their alloys | Gold, Silver, Copper, Brass, Bronze, and their alloys |
| Melting time | 5minutes | 5minutes |
| Max capacity | 24K Gold: 1.2 kg 18K Gold: 1.0 kg 925 Silver: 0.6 kg | 24K Gold: 2.4 kg 18K Gold: 2.0 kg 925Silver: 1.2 kg |
| Max temperature | 1600℃ | 1600℃ |
| Temperature control k-type | Optional | Optional |
| Dimension | 2100*1250*1950mm | 900*1150*2000mm |
| Weight | 680kg | 220 kg |
| Heating technology | Induction heating | Induction heating |
| Cooling way | Water cooling | Water cooling |
- High vacuum (6.67×10-4pa), high vacuum melting, high product density, low oxygen content, no pores, suitable for the production of high-quality bonding wire.
- Anti-oxidation, inert gas protection during refining to solve the problem of alloy oxidation.
- Uniform fineness, electromagnetic and physical stirring methods make the alloy more uniformly colored.
- Smooth surface of the finished product, using a bottom-pulling design, the traction wheel undergoes special treatment, resulting in a flat and undamaged finished product with a smooth surface.
- Precise temperature control ±1℃, using imported temperature control meters, intelligent PID temperature control system, temperature difference ±1℃.
- 7-inch full-color touch screen, more convenient for observation/touch, new system, concise UI interface, easy operation with a single touch.
- Multiple protections, multiple safety protections, worry-free use.
Why SuperbMelt Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine



Any Question About SuperbMelt Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine
Any Question About SuperbMelt Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine
Market Guide: Metal Billets Manufacturing, Applications, and the Value of Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine
Core Requirements for Manufacturing Metal Billets (Rods / Tubes / Plates / Wires, etc.)
I. Core Requirements for Manufacturing Metal Billets (Rods / Tubes / Plates / Wires, etc.)
Metal billets serve as fundamental intermediate products in the high-performance alloy manufacturing supply chain. Their production must precisely match the downstream industries’ differential requirements for material, precision, performance, and capacity, which directly dictates the technological development and configuration of the Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine (VCCM).
1. Raw Material and Purity Requirements
Material Compatibility: Selection of corresponding metals and alloys based on application scenarios, such as nickel-based superalloys and titanium alloys for aerospace 1; copper, silver, and other precious metals for electronics 2; and stainless steel/carbon steel for general machinery.
Purity Control: High-end sectors demand extremely stringent purity, driven by the urgent need for zero-defect materials.1 For example, the impurity content in aerospace superalloys must be below 100 ppm; and electronic-grade copper billets require purity $\ge 99.99\%$.
VCCM Solution: The VCCM utilizes a high-vacuum environment (e.g., $6.67 \times 10^{-4} \text{ Pa}$) for vacuum treatment, which is its core process 3, effectively achieving degassing (removing highly active impurities like hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen) and inclusion removal.1 This ensures ultra-high purity, high density, and pore-free castings.2 VCCM’s associated purification modules can meet various purity standards.
2. Process and Precision Requirements
Dimensional Precision and Surface Quality: Billet quality standards demand internal soundness, chemical homogeneity, and surface integrity.
Dimensional Precision: Rod diameter tolerance generally needs to be controlled within $\pm 0.1 \sim \pm 0.5 \text{ mm}$; wire diameter tolerance is stricter, requiring $\le \pm 0.02 \text{ mm}$. The VCCM must precisely regulate casting speed, cooling rate, and pulling force to ensure dimensional stability.
Surface Quality: High-end billets require surfaces free of scale, porosity, or cracks, with roughness $Ra \le 0.8 \mu \text{m}$. The VCCM’s vacuum environment prevents molten metal oxidation 2, and optimized crystallizer design and cooling systems enhance surface finish.4
Internal Performance and Microstructure: Macro-segregation must be strictly controlled, ensuring uniform chemical composition and fine grains. For high-performance forgings, subsequent forging steps cannot eliminate chemical non-uniformity formed during the casting phase.1
VCCM Solution: Operating in a steady-state, continuous mode, VCCM delivers a steep and precisely controlled thermal gradient, achieving faster solidification rates than large, slow-cooled batch ingots. This rapid and uniform cooling minimizes the Primary Dendrite Arm Spacing (PDAS), resulting in a fine, uniform microstructure, reducing the risk of microporosity and hot tearing, and enabling optimized grain structure control.1
3. Capacity and Automation Requirements
Scalability and Continuity: Industries like automotive, electronics, and construction require materials daily demand exceeding 10 tons. Equipment must support 24-hour continuous operation, with daily capacity of 5–50 tons, and large industrial lines potentially exceeding 100 tons.1
Small-Batch and Customization: Scenarios like laboratory R&D or specialty material production require small-batch capacity (10–500 kg/batch). Equipment must support rapid material and specification changeovers (e.g., 2–4 hours for mold replacement and parameter adjustment).
VCCM Solution: The VCCM utilizes a continuous casting process 5, which enables high-throughput, efficient, and low-energy continuous operation.6 Horizontal VCCM (H-VCCM) is often used for small-diameter rods, tubes, or wires; while Vertical VCCM (V-VCCM) is suitable for large-diameter rods and ingots.1 For high-precision, low-volume applications, vertical casting is typically preferred; for high-speed, high-throughput production, horizontal casting is more suitable.7 The future trajectory of VCCM includes integration with advanced sensor technology and Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms for real-time data analysis and automated defect detection.9
4. Specialized Performance Requirements
Extreme Environment Resistance: Aerospace and military billets require resistance to high temperatures ($\ge 800^\circ\text{C}$) and high pressure, e.g., Inconel 718 tensile strength $\ge 1240 \text{ MPa}$, and CMSX-4 single-crystal alloy tensile strength $\ge 1200 \text{ MPa}$ at elevated temperatures.10 The equipment must be compatible with melting and forming superalloys, controlling the grain structure to enhance high-temperature performance.1
Biocompatibility: Billets for medical implants (e.g., titanium alloy rods) must be free of sensitizing impurities. The equipment requires medical-grade material handling processes and a sterile production environment.1
Electrical/Thermal Conductivity: Electronic-grade copper and silver billets must ensure high electrical conductivity (copper $\ge 98\% \text{ IACS}$). The equipment must minimize oxides and pores in the molten metal to enhance conductive performance.2
Applicable Industries and Products for Metal Billets (Rods / Tubes / Plates / Wires, etc.)
Different types of metal billets, due to their structural properties and material advantages, cover a wide range of fields from traditional industries to high-end manufacturing. The varying demands drive the segmentation and upgrade of VCCM technology.
1. Rod/Bar Applications
| Industrial Sector | Key Alloy Category | Primary Billet Form | Key Quality Metrics (Purity/Structure) | Consequence of Failure | VCCM Impact |
| Aerospace Turbine (Hot End) | Nickel-based Superalloys | Rods/Ingots | Inclusion size ( $<10 \mu \text{m}$ ); Uniform fine-grain structure 1 | Catastrophic engine failure (fatigue/creep) | Superior degassing and inclusion removal in primary melt 1 |
| Precision Machinery | High-Speed Steel / Tool Steel | Rods | Diameter tolerance $\pm 0.05 \text{ mm}$, Surface $Ra \le 0.6 \mu \text{m}$ | Reduced mold precision, shorter lifespan | Optimized crystallizer design to improve dimensional accuracy and surface finish |
| Medical Devices | Titanium Alloys (e.g., $\text{ELI}$) | Rods | Good biocompatibility, absence of internal defects 1 | Biocompatibility failure; premature fatigue fracture | Employs medical-grade purification, features non-destructive testing modules |
2. Tube Applications
Petrochemical Industry: Pipes for oil/gas transport, chemical reactor tubes, requiring stainless steel/corrosion-resistant alloys. Uniform wall thickness (tolerance $\le \pm 3\%$) and resistance to high-pressure corrosion are essential. VCCM must enhance the roundness and wall thickness consistency of the formed tubes.
Medical Field: Infusion catheters, interventional therapy devices, requiring titanium alloys/medical-grade stainless steel. Small inner diameter ($\le 2 \text{ mm}$), high smoothness. VCCM requires micro-channel crystallizers and precise drawing techniques.1
Aerospace: Hydraulic system conduits, requiring superalloys. Resistance to high temperatures ($\ge 600^\circ\text{C}$) and fatigue. VCCM needs to control the internal stress distribution of the tubes.
3. Plate/Slab Applications
Electronics Industry: Circuit board substrates, semiconductor packaging plates, requiring copper/aluminum. Ultra-thin (thickness $\le 0.1 \text{ mm}$), high electrical conductivity. VCCM must optimize the cooling rate to prevent plate deformation.2
Construction Industry: Decorative panels, curtain wall cladding, requiring aluminum alloys. Flat surface, oxidation resistance. VCCM needs to improve plate dimensional stability and surface finish.
Automotive Manufacturing: Body structure plates, engine heat sinks, requiring high-strength steel/aluminum alloys. Lightweight, impact resistance. VCCM must ensure uniform mechanical properties across the plate.
4. Wire Applications
Wire manufacturing is a typical VCCM application, particularly for high-value-added precious metals and semiconductor materials.2
Electronics Sector: Chip bonding wires, circuit board leads, requiring gold/silver/copper. Ultra-fine diameter ($\le 0.05 \text{ mm}$), high conductivity. The high-purity, pore-free castings produced by VCCM are ideal raw materials for high-quality bonded wire.2
Textile Machinery: Textile needles, embroidery thread cores, requiring stainless steel. High toughness, wear resistance. VCCM must enhance the wire’s tensile strength and surface hardness.
New Energy: Battery tab connector wires, requiring copper/aluminum. Low resistance, corrosion resistance. VCCM must minimize internal impurities and pores in the wire.
Core Value Proposition of the Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine (VCCM)
As the core equipment for high-end metal billet production, the VCCM’s value extends across manufacturing, application, and industrial sectors, serving as the crucial link connecting billet manufacturing demands with downstream market applications.
1. Manufacturing Value: Overcoming Traditional Constraints, Achieving Standardized Mass Production
1.1 Superior Product Quality and Purity
VCCM is a highly integrated metallurgical process designed to optimize the casting of high-performance alloys. The melting and solidification processes are consistently maintained under a high vacuum environment , minimizing contact time between the melt and refractory materials, and preventing secondary contamination. This reduces molten metal oxidation and gas absorption, decreasing the oxide inclusion defect rate from over 15% in traditional processes to below 2%.
The steady-state operation of VCCM ensures the high consistency of the solidification front, enabling the production of billets with statistically verifiable, low-variability performance. This continuous forming process enhances billet chemical homogeneity by 30% and reduces internal defect rates by 80%, meeting the stringent performance requirements of high-end sectors.
1.2 Significant Efficiency Innovation and Cost Optimization
The continuous nature and potentially higher capacity and throughput of the VCCM (compared to ESR/VAR batch processes) enable rapid expansion of production capabilities.
| Metric | Vacuum Continuous Casting (VCCM) | Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) | Electroslag Remelting (ESR) |
| Casting Process | Continuous, High Throughput | Batch, Single Ingot | Batch, Single Ingot |
| Material Yield (Yield) | High (90-95%): Minimized hot top/butt end discard loss. | Moderate (80-88%): Significant discard due to segregation. | Moderate (85-90%): Discard required; more melt loss to slag skin. |
| Energy Consumption (Energy Consumption) | Lowest per unit mass: Efficient, continuous operation; lower thermal cycling loss. | Highest per unit mass: Full cooling and reheating required per batch. | Moderate: High power needed to maintain slag superheat. |
| Billet Quality Uniformity | Excellent: Steady-state operation, consistent solidification front. | Good: Differences exist between ingot head, body, and tail due to thermal transients. | Variable: Highly dependent on slag conductivity and cooling water flow. |
Due to efficient, steady-state continuous operation, VCCM’s energy consumption per unit mass is significantly lower than batch processes , and is generally more environmentally friendly than traditional casting methods. Furthermore, by reducing oxidation loss (precious metal loss rate drops from 5%∼8% to 1%∼2%) and minimizing subsequent machining allowance, VCCM significantly reduces raw material waste and processing costs, maximizing efficiency across the entire manufacturing value chain.
2. Application Value: Enabling High-End Innovation
Supporting Key Technological Breakthroughs: The high purity and low-defect requirements for superalloy billets in aerospace, and the precision demands for ultra-fine precious metal wire billets in electronics , are often unmet by traditional equipment. VCCM facilitates the mass production of these high-end billets through vacuum melting and precision forming technologies , driving advancements in engine performance and semiconductor packaging miniaturization.
Mitigating the Hidden Cost of Quality Failure: In the market for extremely high-value high-performance alloys, the assurance of superior initial material quality provided by VCCM significantly reduces the risk of discovering casting defects during the downstream, high-cost machining stages. VCCM investment, therefore, provides a risk hedge for high-value material processing.
Achieving Market Differentiation through Certification Speed: Because VCCM delivers highly consistent material with statistically low variability, the amount of test data and verification time required during the certification process for critical markets like aerospace and nuclear energy is substantially reduced compared to high-variability batch processes.
3. Industrial Value: Driving Sector Transformation and Global Competitiveness
Driving Industrial Structure Transformation: VCCM technology is advancing towards Industry 4.0 integration, including the incorporation of advanced sensor technology and AI algorithms. The equipment is transitioning from “semi-automatic control” to “fully automatic intelligent production” (integrating online inspection , remote operation and maintenance, and data monitoring), driving the metal billet industry’s shift from “labor-intensive” to “technology-intensive”.
Operational Footprint and Sustainability Advantage: VCCM exhibits low energy consumption per unit mass and high material yield. Reduced energy consumption and minimal material waste directly translate into a smaller carbon footprint and superior sustainability metrics. Adopting VCCM enables companies to better align with global sustainability goals.
Proprietary Process Control as a Long-Term Competitive Barrier: The ability to optimize VCCM’s continuous process parameters for specific alloys (including vacuum level, solidification rate, and electromagnetic stirring intensity) constitutes proprietary operational know-how. This unique process knowledge is difficult for competitors relying on standard VAR/ESR processes to easily replicate. Investment in VCCM technology and its specialized operating protocols establishes a lasting competitive barrier for companies in the high-margin advanced materials sector.
FAQ Guide of Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine
- 1. What is the continuous casting technique?
- What is a Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine?
- 3. Which metals can be cast using the Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine?
- 4. How does the high vacuum feature benefit the casting process?
- 5. What role does inert gas play in the casting process?
- 6. How is the alloy's fineness ensured in the casting process?
- 7. What is the significance of the bottom-pulling design in surface quality?
- 8. How precise is the temperature control of the Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine?
- 9. What is the role of the 7-inch full-color touch screen in operation?
- 10. In which industries is the Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine commonly used?
- 11. What safety features does the Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine offer?
1. What is the continuous casting technique?
Continuous casting is a manufacturing process used in the metal industry to produce long, continuous lengths of metal with a consistent cross-section. This technique is commonly employed for metals such as steel, aluminum, copper, and other alloys. Here’s an overview of the continuous casting technique:
Mold Filling:
The process begins with the molten metal being poured into a water-cooled mold. The mold is typically made of copper and has the desired cross-sectional shape of the final product.
Solidification:
As the molten metal passes through the mold, it begins to solidify and take the shape of the mold. The outer layer of the metal comes into contact with the cooled mold, forming a solid skin.
Withdrawal from Mold:
The partially solidified metal is continuously withdrawn from the mold. The withdrawal speed is carefully controlled to allow for proper solidification and prevent defects.
Secondary Cooling:
After leaving the mold, the metal continues to cool through a secondary cooling process. This is often achieved using water sprays or other cooling methods to control the temperature gradient and ensure uniform solidification.
Cutting and Coiling:
Once the metal has solidified sufficiently, it is cut into desired lengths or coiled for further processing. Continuous casting can produce long lengths of metal, minimizing the need for subsequent joining processes.
Continuous casting offers several advantages, including:
Cost Efficiency: It eliminates the need for multiple casting and rolling processes, reducing labor and energy costs.
Improved Quality: The continuous process leads to a more uniform and refined microstructure, resulting in improved mechanical properties of the final product.
Reduced Waste: Continuous casting minimizes material waste compared to traditional casting methods, where excess material is often discarded.
Versatility: It is suitable for various metals and alloys, making it a versatile technique in the production of a wide range of products.
Continuous casting is widely used in the production of various metal products, including billets, slabs, blooms, and other semi-finished goods, which can then be further processed into finished products.
2. What is a Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine?
A Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine is a specialized equipment used for casting metals in a continuous process under high vacuum conditions.
3. Which metals can be cast using the Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine?
The machine is designed to cast a variety of metals, including gold, silver, copper, and their alloys like K gold.
4. How does the high vacuum feature benefit the casting process?
The high vacuum (6.67×10-4pa) helps achieve high product density, low oxygen content, and pore-free castings, ideal for producing high-quality bonded wire.
5. What role does inert gas play in the casting process?
Inert gas protection during refining prevents oxidation issues commonly associated with alloy processing.
6. How is the alloy's fineness ensured in the casting process?
The machine employs electromagnetic and physical stirring methods, ensuring a uniform fineness throughout the cast alloy.
7. What is the significance of the bottom-pulling design in surface quality?
The bottom-pulling design, along with specially treated traction wheels, results in a smooth surface on the finished product with no damage.
8. How precise is the temperature control of the Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine?
The machine maintains precise temperature control with an accuracy of ±1℃, using an imported temperature control meter and an intelligent PID temperature control system.
9. What is the role of the 7-inch full-color touch screen in operation?
The 7-inch full-color touch screen provides a convenient interface for observation and operation, featuring a new system and a user-friendly UI.
10. In which industries is the Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine commonly used?
This machine finds application in industries such as jewelry casting, precious metal processing, and university laboratories.
11. What safety features does the Vacuum Continuous Casting Machine offer?
The machine incorporates multiple safety protections, ensuring worry-free and secure operation in various casting processes.




 © Copyright 2008-2026 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited
© Copyright 2008-2026 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited