Laser Welding Machine Cost
Top Manufacturer in China - With the power is 150-200w optional - Convenient power supply: AC 1-P 220V±5%/50Hz
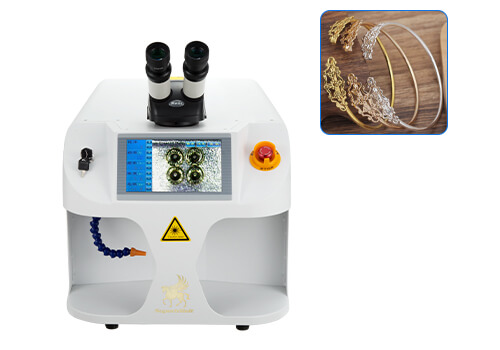

Superbmelt laser welding machine is used to weld and repair noble metals. The laser welding machine for sale by Superbmelt is used in the jewellery making industry to repair broken jewellery items or create complex jewellery items. The laser welder can be used to repair metals such as karat gold, sterling silver, base metals, titanium, etc.
Superbmelt laser welding machine performs a clean, fast and efficient metal repair. The 1064 wavelength of the welding machine makes the laser focus on the spot for perfect repairing. The laser soldering machine is used in jewellery making and repairs, dental fixtures, medical equipment, etc.
The laser welding machine cost is affordable and provides long-lasting use. Contact Superbmelt for the best laser welder machine for sale.
| Model | SPB-150WB |
| Wavelength | 1064nm |
| Max output power | 150W |
| Max pulse energy | 80J |
| Pump source | Single lamp |
| Pulse width | 0.1-20ms |
| Pulse frequency | ≤50Hz |
| Aiming and positioning | Microscope + camera system |
| Application | Welding and repairing various precious metal trinkets |
| Host power consumption | ≤5KW |
| Electricity demand | AC220V±5%/50Hz |
| Cooling system | Water cooling + air cooling |
| Dimension | 660x385x435mm |
| Weight | 49kg |
The mini laser welding machine is a compact laser machine used for welding metal parts. The maximum power required for efficient welding is 150W and a pulse width of 0.1-20ms. The wavelength for welding is 1064nm. The laser welder has a camera and microscope that ensures efficient and high-quality welding. The laser welding machine cost is affordable and long-lasting. It is used to repair jewellery, antiques and complex jewellery, etc.
Parameter
- Power: 150W
- Pulse width: 0.1-20ms
The desktop laser welding machine is a compact-sized machine used to repair or weld metals. The maximum power required for welding is 200W and a pulse width of 0.3-20ms. The minimum spot diameter is about 0.2mm. The camera and microscope make the welding process easy to control to achieve perfect welding. The laser welding machine cost is affordable for all businesses. It is used in the jewellery, medical industries.
Parameter
- Power: 200W
- Pulse width: 0.3-20 ms
The split jewellery welding machine is an industrial size laser welder with a separate water chiller. The split laser welder repairs or welds jewellery items with a maximum power of 200W. The pulse width is 0.1-20ms and the wavelength is 1064nm. The microscope and camera make the welding process efficient. The laser welder makes a clean, fast and non-noticeable repair on expensive jewellery. It is used in jewellery making and repairs.
Parameter
- Power: 200W
- Pulse width: 0.1-20ms

2 years warranty
The warranty for our machine is one year longer than the warranty provided by other factories.

Strong service team
We will give response within 24 hours against your problem by our professional engineer.
Why SuperbMelt Laser Welding Machine Cost



Any Question About SuperbMelt Laser Welding Machine Cost
Laser Welding Machine Cost: Complete Buyer’s Guide
Why do users search for laser welding machine cost?
- Entrepreneurs & Small Business Owners: Such as jewelry workshop founders or small hardware processing plant managers, who need to confirm equipment investment feasibility and avoid overspending on unnecessary functions.
- Manufacturing Procurement Personnel: Responsible for updating production lines, requiring accurate price data to compile budgets and compare suppliers.
- Industry Newcomers: Exploring equipment options for project initiation, needing to understand price ranges to match their technical needs and financial capacity.
Price ranges of laser welding machines
2.1, Jewelry laser welding machines(150–300W)
- Core Application: Welding precious metal jewelry (gold, silver, platinum), such as chain links, settings, and small components.
- Price Range: 5,000–18,000
- Entry-level (150W): 5,000–8,000 (suitable for small workshops, manual operation, basic spot welding for thin materials ≤1mm).
- Mid-range (200–250W): 8,000–12,000 (semi-automatic, precise spot control, compatible with 0.3–2mm metals, ideal for jewelry chains and pendants).
- High-end (300W): 12,000–18,000 (automatic positioning, micro-welding capability, low metal loss ≤1%, suitable for luxury jewelry brands).
- Key Features: Compact design (saves workspace), low energy consumption, and laser spot diameter ≤0.3mm for delicate welding.
2.2, Handheld fiber laser welding machines(1000–2000W)
- Core Application: Medium-thickness metal processing, such as hardware fittings, stainless steel products, and small structural parts.
- Price Range: 12,000–35,000
- 1000W: 12,000–18,000 (welds 1–3mm stainless steel/aluminum, suitable for small hardware factories).
- 1500W: 18,000–25,000 (welds 2–5mm metals, faster speed, widely used in kitchenware and furniture manufacturing).
- 2000W: 25,000–35,000 (welds 3–8mm thick plates, portable design for on-site maintenance and large workpieces).
- Key Features: Handheld operation (flexible for irregular workpieces), no need for complex fixtures, and high welding efficiency (3–5x faster than traditional methods).
2.3, Industrial laser welding machines (3000–6000W)
- Core Application: Large-scale industrial production, such as automotive parts, shipbuilding, and steel structure welding.
- Price Range: 50,000–200,000
- 3000–4000W: 50,000–100,000 (welds 5–12mm thick metals, automated production lines, suitable for medium-sized manufacturers).
- 5000–6000W: 100,000–200,000 (high-power continuous welding, welds 8–20mm plates, used in heavy industry and large equipment manufacturing).
- Key Features: High automation (integrated with robotic arms), long continuous operation time (24/7), and high welding strength (meets industrial standards like ISO 13919).
2.4 YAG spot welding machines (older models)
- Core Application: Low-demand scenarios, such as small-scale electronic component welding or hobbyist use.
- Price Range: 3,000–8,000
- Pros & Cons: Low initial cost, simple operation; but low efficiency, high energy consumption, and limited to thin materials (≤0.8mm). Gradually being replaced by fiber laser machines in industrial settings.
Why is there such a big price difference?
The price gap between laser welding machines (from 3kto 200k) stems from four core factors:
3.1, Different laser types
- Fiber Laser (Mainstream): Accounts for 80% of the market. Advantages include high energy conversion rate (30–40%, vs. 10–15% for YAG), long lifespan (100,000 hours vs. 10,000 hours for YAG), and low maintenance. Machines using imported fiber modules (e.g., IPG, Raycus) are 30–50% more expensive than those with domestic modules.
- YAG Laser (Outdated): Lower cost but higher energy consumption and frequent replacement of pump lamps (costly over time).
- CO2 Laser: Rarely used for metal welding; mainly for non-metallic materials, with high prices ($80k+), not included in mainstream metal welding options.
3.2, Different laser power levels
- Low power (150–300W): Simple circuit design, small cooling system, low material cost.
- High power (3000–6000W): Requires large cooling systems (water-cooled, 5k–15k alone), reinforced mechanical structures, and high-power laser sources (costing 20k–50k), driving up overall prices.
3.3, Three core components that determine the price
- Laser Source: Imported fiber sources (e.g., IPG from the US, Trumpf from Germany) cost 2–3x more than domestic ones (e.g., Raycus, MAX). A 2000W imported source costs 15k–20k, while a domestic one costs 5k–8k.
- Welding Head: Precision welding heads (e.g., Precitec, Soudax) with auto-focus and beam adjustment cost 3k–8k, vs. 500–2k for basic domestic heads.
- Control System: CNC control systems (e.g., Siemens, FANUC) for automated machines cost 10k–30k, while manual machines use simple PLC systems (1k–3k).
3.4, Different automation levels
- Manual Machines: No need for fixtures or robotic arms, low cost (e.g., handheld 1000W machines at 12k–18k).
- Semi-Automatic Machines: Equipped with worktables and simple fixtures, cost 30–50% higher than manual models (e.g., 200W jewelry machines with auto-positioning at 8k–12k).
- Fully Automatic Machines: Integrated with robotic arms, vision systems, and production line integration, cost 2–5x more (e.g., 3000W robotic welding lines at 100k–150k).
Hidden costs of laser welding machines
Initial purchase price is just the tip of the iceberg—hidden costs over 3–5 years can account for 20–40% of the total investment. Be sure to factor these in:
4.1, Consumable costs
- Laser Source Components: Fiber laser modules have a lifespan of 50,000–100,000 hours; replacement costs 5k–20k (domestic) or 15k–40k (imported). YAG lamp replacements cost 500–1k every 1,000 hours.
- Welding Head Parts: Focus lenses (200–800 each, replaced every 6–12 months), protective windows (50–200 each, replaced monthly for high-volume production).
- Auxiliary Materials: Shielding gas (argon, 50–100 per cylinder, 1–2 cylinders monthly for small workshops), cooling water additives (100–300 annually).
4.2, Maintenance costs
- Routine Maintenance: Professional inspections (twice a year, 500–2,000 per visit), cleaning of optical components, and calibration of laser paths.
- Repair Costs: Circuit board repairs (1k–5k), cooling system maintenance (500–1,500 annually), and robotic arm servicing (for automatic machines, 5k–10k every 2 years).
- Downtime Loss: Unexpected breakdowns can halt production—for a medium factory with 10kdailyoutput,a3−dayrepairtranslatesto30k in lost revenue.
4.3, Energy consumption costs
- Power Consumption: Low-power machines (150–300W) use 1–3kWh/hour; high-power machines (3000–6000W) use 10–25kWh/hour (plus cooling systems).
- Calculation Example: A 2000W handheld machine operating 8 hours/day, 250 days/year, at 0.15/kWh:Annualenergycost=2000W×8h×250d×0.15/kWh ÷ 1000 = 600.A5000Windustrialmachineoperating24hours/day:Annualenergycost=5000W×24h×300d×0.15/kWh ÷ 1000 = $5,400.
How to choose the right laser welding machine?
5.1, For the jewelry industry
- Key Requirements: Precise micro-welding, low metal loss, compact size, and compatibility with precious metals (gold, silver).
- Recommended Models: 150–300W fiber laser welding machines.
- Small Workshops (Budget 5k–8k): 150W manual models (e.g., JPT 150W) for basic chain and pendant welding.
- Medium Jewelry Factories (Budget 8k–15k): 200–250W semi-automatic models with auto-focus (e.g., Raycus 250W) for high-precision production.
- Luxury Brands (Budget $15k+): 300W high-end models with vision positioning (e.g., IPG 300W) for minimal loss and flawless welds.
- Tips: Prioritize machines with low metal loss (<1%) and pulse welding mode (avoids overheating precious metals).
5.2, For hardware processing factories
- Key Requirements: Versatility (weld stainless steel, aluminum, copper), moderate thickness capacity (1–8mm), and portability.
- Recommended Models: 1000–2000W handheld fiber laser welding machines.
- Small Factories (Budget 12k–18k): 1000W handheld models (e.g., MAX 1000W) for small batches and on-site repairs.
- Medium-Scale Production (Budget 18k–30k): 1500–2000W models (e.g., Raycus 2000W) for faster speed and thicker materials (up to 8mm).
- Tips: Choose machines with adjustable laser modes (continuous/pulse) for different materials—aluminum requires higher power and pulse mode to avoid porosity.
5.3, For heavy industry
- Key Requirements: High power, continuous operation, automation, and compliance with industrial standards.
- Recommended Models: 3000–6000W fully automatic laser welding machines (integrated with robotic arms).
- Medium Manufacturers (Budget 50k–100k): 3000–4000W robotic welding lines (e.g., Trumpf 3000W) for 5–12mm thick plates.
- Large Enterprises (Budget 100k–200k): 5000–6000W high-power models (e.g., IPG 6000W) for heavy-duty welding (ships, automotive frames).
- Tips: Prioritize machines with CE/ISO certification, 24/7 operation capability, and remote monitoring (reduces maintenance downtime).
FAQ Guide of Laser Welding Machine
- 1. How is jewelry welded nowadays?
- 2. In which cases does jewelry need to be welded?
- 3. The advantages of the laser welding method for jewelry compared to other existing methods
- 4. Why are laser welding machines required to weld jewelry?
- 5. The method of processing laser-welded jewelry
- 6. What are the core components of the laser welding method, and how should one maintain them?
- 7. What materials can be laser-welded?
- 8. Does laser welding weaken metal?
- 9. What kind of laser welding machines can one use to repair jewelry?
- 10. Where is the method of laser welding used?
- 11. Can aluminum be laser-welded?
- 12. What is the strength of laser-welded jewelry?
- 13. The principle of laser welding machines
- 14. What are the tools available in the market for the repair of jewelry?
- 15. Why are laser welding machines the best option for welding jewelry?
1. How is jewelry welded nowadays?
Nowadays, laser welders are a hot product in the market. Factory workers use welding machines to weld various materials. One of the most general uses of welding machines is in welding jewelry. The average laser machine cost is about 20k to 30k (as recorded in recent years).
In the industrial sector, the use of welding methods for jewelry welding has become a time-honored tradition. Over time, more people have gained employment in this segment of society. A start-up business associated with soldering jewelry is advantageous due to laser welder cost being quite reasonable in the market.
Jewelry welding has already made a significant impact on the future of our industry. Jobs such as strengthening metals by joining, soldering jewelry on-demand, and repairing old jewelry are the most common for professional welders.
A great benefit of jewelry welders is building customer loyalty. Through this profession, employers earn a good reputation and respect from clients. It shows that the craftsmen are innovative and updated on the latest technology.
Jewelry welding is the most desirable job in this area of industrial employment. Soldering metals from aluminum to welding platinum, all fields are equally in demand in the current society.
2. In which cases does jewelry need to be welded?
Jewelry containing broken parts such as clips, clasps, and cuffed edges needs to be welded. The welding method is a DIY solution to fix these broken pieces and solder them together to make the jewelry more durable and long-lasting.
The key to successfully weld jewelry:
- Preparing your workspace
An efficient job always accounts for a good work area. Hence it is necessary to have a clean and flat work area that is well ventilated.
- Be safe than sorry
Soldering jewelry is easy to learn, but when dealing with high-heat types of equipment, you need to be aware of your safety. Working with gloves on in a work-ready environment is the best plan.
- Preparing the Jewelry
As a welder, one needs to know the properties of metals you have decided to use. Sometimes they may not be compatible, and the project may end up being a failure. Hence, you need to plan first and then start.
- Applying Flux and Heating
Applying flux to the area that needs welding is advisable to achieve better results. After this comes heating the connecting points quickly with a torch.
Regulation of heat is vital in this step since overheating can melt the jewelry piece.
- Quenching the Metal
After the jewelry piece is done welding, place it in a jar filled with water to help it cool down. This process is called ‘quenching.’
- Checking the Bond
Lastly, it is imperative to check the bond of your jewelry before sending it out for the packaging process.
3. The advantages of the laser welding method for jewelry compared to other existing methods
The laser welding method is an advanced metal welding technique that utilizes a focused laser beam. During the welding processes, the laser melt surrounds the workpiece and the filler material to form accurate welds.
There are various traditional welding techniques still used in today’s world. They are stated below:
- TIG or Tungsten inert gas welding:This type of welding method applies a non-consumable tungsten electrode to the workpiece’s heating and melting the filler (if any) to compose the weld.
- MIG or Metal inert gas welding:This welding method utilizes a consumable wire component that serves as both the filler element and the electrode and in producing the weld.
- Spot-welding Method:This welding process employs two electrodes to solder items and passes an electric current between them to form the weld.
Compared to conventional welding methods, the laser welding method has the following advantages:
- Less heat generation:In laser welding operations, the HAZ zones or heat-affected zone is considerably smaller. The cumulative heat input is much lower than the traditional welding operations.
- Lower risk of macro distortions:There is a lower risk of distortion originating from heat input. Less heat indicates less thermal stress. As a result, it causes minor damage to the workpiece.
- Express processing time:Despite its higher fundamental investment, laser welding can often prove extra cost-effective than traditional welding due to its accelerated processing speed. More speedy production also means more extraordinary production abilities, resulting in a quicker success rate.
- Better suited for thin metals:Due to its spot size, laser welding is an excellent joining technique for welding thin or delicate metal parts. The spot size can be explicitly designed only to meet the proper expectations and aid in melting the amount of metal needed to achieve the weld, thus reducing heat-induced inner stresses, deformities, and errors.
4. Why are laser welding machines required to weld jewelry?
Small laser welding machine price in the market is very reasonable. They are used to weld jewelry because of the various advantages they offer. Jewelry has minute details, and laser soldering provides top-notch precision.
The use of small laser welding machine price being low, its use in welding jewelry is also effective since they are easier to maintain and cost-effective.
Jewelry is made of various alloys, metals, and precious stones; the method of soldering jewelry is used most often since welders and artisans could not use pre-existing methods in welding all types of metal, such as titanium.
Laser welder cost is average, and welders can choose from a plethora of options available in the market.
5. The method of processing laser-welded jewelry
Laser welding involves a highly concentrated beam of laser light on a very minute spot so that the expanse under the laser beam receives the light and grows to be highly energetic.
Since powerful laser beams are utilized, the electrons in the peripheral area get excited to such a point where the element melts due to the breaking of atoms’ bonds with other atoms. Laser welding can be used to join metals and also plastics.
This melting of a pair of materials at their joints blends them into a particular element. It is remarkable how a source of light can be strong enough to metal metals within mere seconds. The mini laser welding machine price is reasonably practical, and it uses numerous parts that amplify and direct the laser light to achieve such powerful laser beams.
The three most popular types of lasers used in a laser welding machine in today’s society are solid-state lasers, gas lasers, and fiber lasers.
Usually, the laser beam is provided to a laser welding machine by the application of optical fibers. There are single fiber welding machines, and there are multiple fiber welding machines designed for different purposes. The numerous fiber welding machines have a laser attached to each fiber, and it helps the strength of the laser increases.
A collimator lens combined with a focusing lens is frequently used to direct the beam to a point before leaving the machine.
Four joints that can be done with laser welders are:
- Filler Lap Weld
- Edge Flange Weld
- Overlap Weld
- Butt Weld
6. What are the core components of the laser welding method, and how should one maintain them?
The complete form of Laser is Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. It is a non-contact method that needs to access the weld zone from the side of the welded pieces.
The main types of lasers used in welding and cutting are:
- Gas lasers: use a blend of gases like helium and nitrogen. These lasers use a low-current, high-voltage power source to stimulate the gas mixture utilizing a lasing medium that operates in pulses or continuous mode.
- Carbon dioxide lasers blend high purity carbon dioxide with helium and nitrogen as their lasing medium. CO2 lasers are additionally used in dual-beam laser welding, where the beam is divided into two equal power beams.
- Solid-state lasers: The pulsed movement produces joints similar to spot welds but with total penetration. The pulse energy can go up to 1 to 100 Joules.
- Diode lasers: Lasers that are used for materials that are tricky to weld using other methods, for hard-to-access areas, and tiny components. Inert gas shielding is needed for more reactive materials.
To maintain the components of a laser welding machine, they should look out for laser welding machine cost, quality, keeping the benchmark light source in check, and adjusting the input/outputs.
7. What materials can be laser-welded?
Pulses that last a millisecond are used for welding thin materials like razor blades, while continuous laser operations are engaged in deep welding of the workpiece. Laser Welding is a multifaceted process that is capable of welding the elements as stated below:
- Stainless steel: Stainless steel is quite difficult to solder. Silver bearing solder and the high activity flux are specially designed for welding stainless steel.
- HSLA steels: High-strength low-alloy steel can also be soldered using the process of laser welding. The laser welder costbeing relatively low, it is suited to weld HSLA steel.
- Aluminum: TheLaser beam welding machine price is 20k. It is the traditional method for welding aluminu The heat-affected zone is reduced, and weld penetration raises to 0.25”.
- Carbon steels: Due to laser welding machine costbeing reasonable, one can also weld carbon steel with other m
- Titanium: Titanium was previously impossible to solder. Now, we can use laser welding technology.
8. Does laser welding weaken metal?
The most important thing to consider in the process of welding is whether the metal being used will become weaker as the welder joins it with another metal.
Welding can weaken steel, alloys, and other precious metals, particularly in the HAZ or the heat-affected zone, if welding is performed at high temperatures. Weakening in the process of welding is the most common with cold-rolled steel.
Laser welding, on the other hand, has the ability to adjust the temperature according to use. So, the heat regulation feature helps welders to control the temperature during the soldering of metals.
9. What kind of laser welding machines can one use to repair jewelry?
Various machines are available in the market that is used for soldering metal and repairing jewelry. The Laser soldering machine cost around 30k in the current market, and it is perfect for welders who repair jewelry.
10. Where is the method of laser welding used?
The method of Laser welding is used in various sectors in the industrial niche of society.
- It finds prominent usage in the automotive and industrial sectors. It is used mainly in those areas where a large volume of products are being manufactured.
- It is applied for high-precision welds. Because it does not use any electrode, the final weld is light but very high in strength.
- Laser welding finds frequent usage in the making of jewelry and related areas of work.
- However, laser beam welding tool price is lower in the market. It is used extensively in medical industries to hold metals together on a relatively more minor scale due to laser beam welding tool price being low.
11. Can aluminum be laser-welded?
Laser welding is extensively used to join aluminum and its alloys. Though, aluminum poses challenges in welding due to three of its main properties as listed:
- Thermal conductivity.
- Its reflectivity of surface to infrared and near-infrared laser light radiations.
- All the properties of the molten alloy comprise low viscosity and low boiling point of alloying elements used with aluminum—for example, metals such as Magnesium, Zinc, and others.
These and other material-related challenges can lead to weld and heat-affected zone cracking, degeneration in the mechanical properties, and discrepant welding performance.
However, laser welding does a great job.
The principle of laser beam welding
Working Principle
It works on the principle where electrons of an atom get excited by absorbing energy. And then, after some time, as it returns to its ground state, it transmits a photon of light. The concentration of this emitted photon is amplified by incited emission of radiation, and a high-energy concentrated laser beam is obtained.
Amplification of light by incited radiation is known as a laser.
Main Components
The main components or equipment of laser beam welding are:
A laser machine is a type of machine used to produce a laser beam for welding. Its main components are:
- Power Source:A high-energy power source is utilized across the laser machine to generate a laser beam.
- A.M.:It is a computer-aided manufacturing method in which the laser machine is united with the computers to complete the welding process. C.A.M. does all the controlling action during the welding process by laser and speeds up the welding method to a more significant degree.
- A.D.:It is called Computer-aided Design. It is adopted to plan the welding process. Computers are used to develop the item and how to design its performance.
- Shielding Gas:A shielding is used to restrict the piece from oxidation.
12. What is the strength of laser-welded jewelry?
Laser welding is more frequently used in extensive industrial methods as it creates less heat and has more comprehensive applications than the traditional welding methods. Besides, the laser beam is very focused, which means that heat transfer to the piece is considerably less, and the whole structure is less affected. The quality of the weld is more compelling compared to traditional methods of welding.
Laser welding is a much more accurate manufacturing process, and the welds can be as small as one-hundredth of a millimeter. Tiny pulses of heat are used to create the weld, which leads to a more extraordinary quality finish that is stronger and provides a better depth-width ratio. Depending on the laser power, welders can accomplish welding penetration up to fifteen millimeters of stainless steel or standard steel.
Another mention-worthy advantage of laser welding compared to other methods is that- laser beams can weld a more extensive variety of metals such as high-strength stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, platinum, various alloys. Precious metals such as silver and gold can also be soldered together through this process.
In the method of laser welding, welds are much more precise, and the finish is superior. Therefore, the production process is excellent for delicate components, and welders can use it in various areas where the welder has limited access. Lasers enable the correctness and quality required for thin soldered pieces.
The strength of jewelry soldered by the process of laser welding has extraordinary strength and durability as compared to other methods.
13. The principle of laser welding machines
To get better at welding metals, a welder should know about the principle of Laser Welding. The role of a laser is to magnify the light source. Regular light sources cannot be used as laser light since the radiating energy from a common source of light is inconsistent and scattered over a wide spectral range. The standard light source of monochromatic single-color sources does not exist.
Due to irregularity in the wavelengths of different colors composing familiar light sources, combining it into a sharp focus without cutting intensity is impracticable.
Therefore, for its performance, the laser depends upon the emanation of radiation, induced or incited by the absorption of particles of energy or electromagnetic energy, termed as photons, by the atoms. When this energy is intercepted, the electrons in the atom increase their rotation and extend their orbits, prompting them to go into a state of excitement.
This excited state is short-lived, and the atom instantly drops back to an intermediary level or metastable state. In this process, the particle loses its heat energy but maintains its photon energy. Soon after, the particle falls automatically and randomly back to its previous ground state, liberating the quantum energy, or photon energy.
14. What are the tools available in the market for the repair of jewelry?
There are many tools available that can help to repair jewelry and save loads of time.
- Eye Loupe
Using an eye loupe is vital when it comes to precision in jewelry repair. Hands-Free LED Eye Loupe comes with an adjustable head strap, 6x magnifying lens, and an LED light for ultimate accuracy and visibility. The Hands-Free LED Eye Loupes with magnifying lenses, LED lights, and adjustable straps are perfect for this job. Eye Loupes are available for various purposes.
- Heavy Duty Shears
When welders want to repair the order or structure of beads in a jewelry piece, they need to cut jewelry, and finding a durable pair of shears can do their job efficiently.
- Pliers
Pliers are great for working with curving and looping wire and picking up beads. They are available in different sizes to suit the welder’s needs.
- Bead Tubes
Bead tubes are come in handy when welders need to organize thousands of beads in order. They are a great option to save time and effort on pieces a welder is working with.
15. Why are laser welding machines the best option for welding jewelry?
Laser welding machines are by far the best available solution in the market in soldering jewelry. A fibre laser welding machine price is arguably lower than such other machines, making laser welding machines the most sought-after option in the industrial niche.
The reasons that cater to considering mini laser welding machine price is cheap, and they are the best option for welding jewelry are:
- Strength of the weld: The laser welds are narrow and have an excellent depth-to-width ratio. They are also higher in strength compared to other methods.
- Limit of heat-affected zones: Due to rapid cooling, the heat-affected zones are limited, and the metal surrounding is not tempered.
- Welding various metals together:Laser machines weld metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, precious metals, and even dissimilar metals.
- Precision: Laser beams are well-controlled, and their micro-welding feature helps achieve accuracy.
- Physical Contact: There is no physical contact between the laser head of the machine and the material.
- Deformation: Deformation is least in this process.
- Waste:Fibre laser welding machine price is comparatively low, and laser welding generates very minimal volumes of waste as compared to other methods used in welding jewelry.






 © Copyright 2008-2026 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited
© Copyright 2008-2026 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited