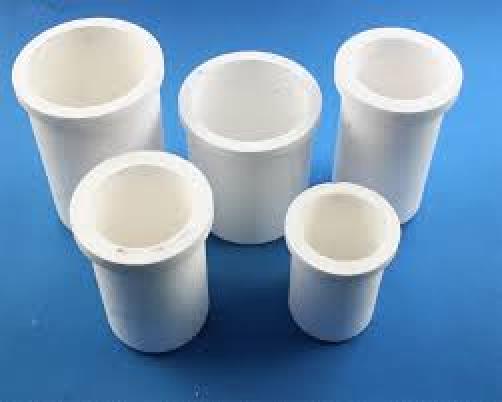
Furnace Crucibles
Top Furnace Crucible Manufacturer in China
- Designed for 1-30kg gold/silver/copper smelting
- Top quality, durable crucible supplier
- As the source factory, large inventory, fast delivery
Get Price For Batch Order (MOQ 10pcs)
Top Furnace Crucible for Sale
A furnace crucible is used for melting and casting of metals and certain alloys. This is the part of the induction furnace that holds molten metal during melting processes. The furnace crucible is made up of graphite which makes it a high quality induction furnace graphite crucible. The furnace crucible is best applicable to the induction melting furnace. The high density body of the furnace crucible and its structure makes the furnace crucible a better compression property. This furnace crucible has a very high resistance to corrosion, therefore, making it a better anti-corrosion crucible than the common clay crucible.
The advanced process improves its oxidation resistance, which gives a persistent heat conductivity and a longer melting life. The induction furnace graphite crucible manufacturers ensure that the graphite furnaces are energy-efficient, that is, it requires low energy at the same time, pollution-free, this does not only ensure metal purity but also ensures a sustainable environment.




SuperbMelt Furnace Crucibles list
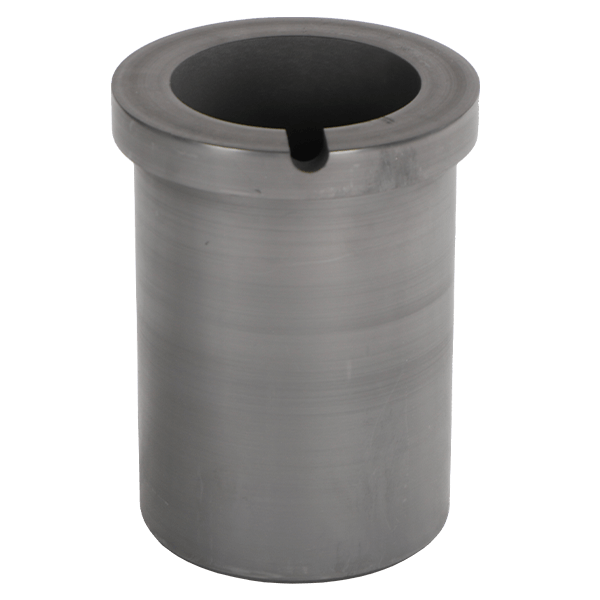

Graphite crucibles are high quality melting crucibles. Graphite crucibles are used at temperatures reaching 1600 degree celsius and they are suitable for smelting in the precious metal smelting furnace. Graphite crucibles are also used for melting and holding base metals and their alloys. Graphite crucible properties include; superior thermal conductivity, strong corrosion resistance that prolongs crucible life, low energy consumption, resistance to acidity and alkalinity, no pollution, excellence chemical stability.
Parameter
- Melting Capacity: 1-30kg
- Application: gold, silver, copper, iron etc.
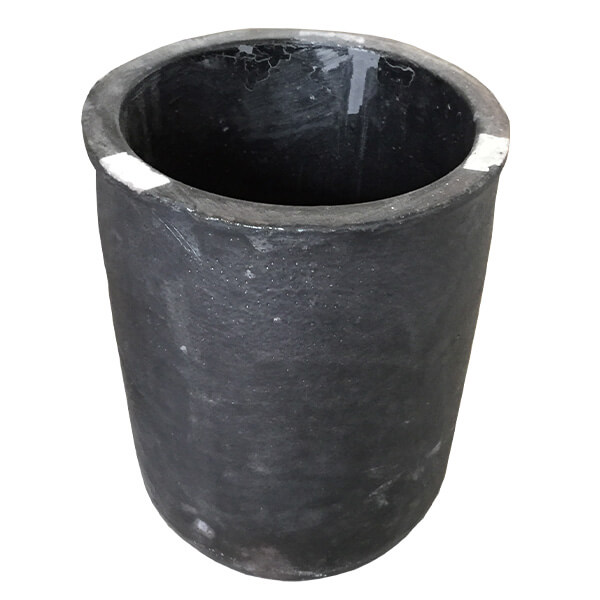

The silicon carbide graphite crucible is used for smelting and melting precious metals in the precious metal smelting furnace at 1600 degree celsius. Silicon carbide graphite crucible has the following outstanding characteristics; excellent thermal shock resistance, electrical and thermal conductivity, good wear resistance, high graphite material purity, high crucible density, high mechanical strength, strong chemical stability. Silicon carbide crucibles have resistance to acidity and alkalinity from fluxes and additives.
Parameter
- Capacity: 1-250kg
- Application: gold, silver, copper, iron etc.
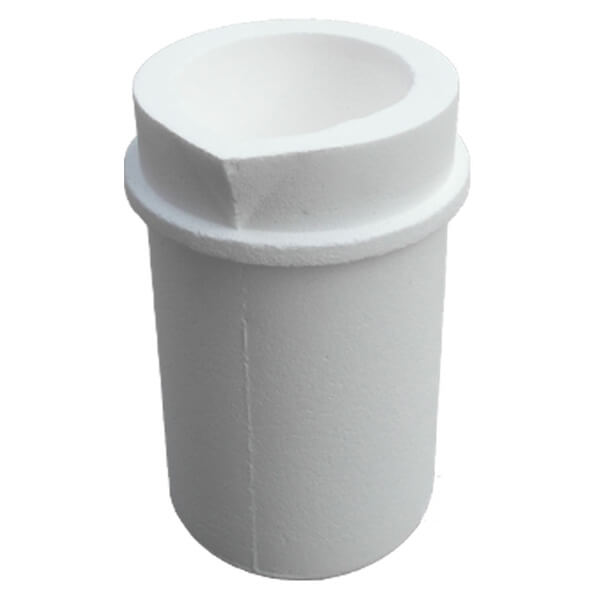

Quartz crucible
Quartz crucibles are used to melt high temperature precious metals such as platinum, palladium and special alloys in the precious metal smelting furnace at above 1700 degree celsius. Quartz crucibles are resistant to extremely high temperatures, they are also chemically inert to get non-contaminable results. Other quartz crucibles properties include; resistance to thermal shock, corrosion resistance, excellent casting quality of precious metals.
Parameter
- Capacity: 1-10kg
- Application: Platinum, Palladium, Steel, Gold etc.
Why SuperbMelt Furnace Crucible
High Quality
Why You Could Choose SuperbMelt

AAA credit audited enterprise
The government Audited Superb as AAA credit company (top level).

ISO CE SGS approved
Professional certification bodies certify that the machines are of high quality.

Strong service team
We will give response within 24 hours against your problem by our professional engineer.
Any Question About SuperbMelt Graphite Molds
Superbmelt’s professional technical team and sales team are at your service
(7/24hours service)
How to Choose Graphite Crucible: Furnace Crucibles Buying Guide
How Many Types of Furnace Crucibles Are in the Market
There are different types of furnace crucibles made from different properties. The most popular and commonly used furnace crucibles are; graphite crucible, clay graphite crucible, silicon carbide crucible, platinum crucible, porcelain crucible and metal crucible. These crucibles are termed according to the raw materials they are made from.
The main market for furnace crucibles is the foundry industry used for melting and testing metal. Crucibles are also used for chemistry research. With the growing metal and metal production industry, the need for specialized metal and alloy casting is increasing day by day and durable and efficient furnace crucibles are needed to carry out melting and casting activities.
1.1, Graphite Crucible
Graphite furnace crucibles are refractory containers specially shaped for metallurgical operations. Graphite furnace crucible is primarily made of graphite material that is typically grayish-black in colour, opaque, and has a radiant blaack sheen. The properties of the graphite furnace crucible distinguishes it from other types of furnace crucibles.
The graphite material that makes up the graphite furnace crucible itself is tightly fused together and no part becomes loose when metal is being melted, therefore, your metal is protected from contamination. Graphite furnace crucibles can withstand high melting temperatures of metal up to 1600 degree celsius.
Graphite furnace crucibles have good resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal shock. There is a good demand for graphite furnace crucibles based on the assessment and growth in foundry and casting industries. Graphite crucibles are used to melt ferrous, non ferrous metals and alloys can be melted and smelted using a graphite furnace crucible.
Graphite crucibles prevent contamination of molten metal when melting and holding metals. Other properties of the graphite furnace crucible include:
Thermal stability: The graphite furnace crucible is able to withstand the changing temperatures of metals during the melting and holding process.
Corrosion resistance: The uniform and dense design of the graphite furnace crucible can effectively prevent corrosion of the graphite furnace crucible.
Impact resistance: The impact strength that graphite furnace crucible can bear is very high, therefore, any further process can be done easily.
Acid resistance: Special materials such as flux and additives are added to molten metal in the crucible in order to improve the melting quality of such metal, this means that graphite crucible needs to be able to withstand the effects of additives and fluxes, this therefore greatly extends the life of graphite crucible.
High thermal conductivity: The high content of fixed carbon ensures good thermal conductivity of the graphite furnace crucible, and reduces the time of dissolution or melting, significantly reducing fuel consumption, or other energy consumption.
Metal pollution control: The material composition is strictly controlled to keep the metal from being polluted by the graphite crucible.
Quality stability: High pressure forming method and quality assurance system fully ensures the high quality molten metal.
1.1.1. Pure Graphite Crucible
Pure graphite furnace crucible is made of 99.9% of graphite. Its features include excellent thermal stability and great heat transfer performance for fast heating and cooling and corrosion resistance to strong acid and alkali. Pure graphite furnace crucible is used to melt and cast metals such as gold, silver brass, aluminium, copper, zinc, etc. Pure graphite furnaces cannot be heated by a carbon furnace or charcoal kiln, it will oxidize and crack if any of these furnaces is used.
Pure graphite starts to oxidize at 400 degree celsius and they withstand temperatures 1760 degree celsius when used in an air electric furnace. The withstand temperature in a vacuum or gas protection furnace is 2760 degree celsius. Graphite furnace crucible is generally used in alloy tool steel smelting and smelting of nonferrous metals and their alloys. Graphite is more durable than ordinary material products, which makes graphite furnace crucible to have a long service life under correct use.
1.1.2. Silicon carbide graphite crucible
Silicon carbide graphite furnace crucibles are high quality melting crucibles made out of silicon carbide and graphite. Typical silicon carbide characteristics include: low density, high strength, good high temperature strength (reaction bonded), oxidation resistance, excellent thermal shock resistance, high hardness and wear resistance, excellent chemical resistance, low thermal expansion, refractory material (high melting point) and high thermal conductivity. Silicon carbide possesses interesting electrical properties due to its semiconductor activities.
Silicon carbide is formed in two ways, reaction bonding and sinistering. Each forming method greatly affects the end microstructure. Reaction bonded silicon carbide is made by inflitering compacts made of mixtures of silicone carbide. And carbon with liquid silicon. The silicon reacts with the carbon forming more silicon carbide which bonds the initial silicon carbide.
The sintered silicon carbide is produced from pure silicon carbide powder with nonoxide sintering aids. Conventional ceramic forming processes are used and the material is sintered in an inert atmosphere at temperature reaching up to 2000 degree celsius or higher.
Both forms of silicon carbide are highly wear resistant with good mechanical properties.
The raw materials, graphite and silicon carbide with additives such as ferro silicon, ferro manganese etc, are graded to the required sizes and mixed with bounding materials like molten pitch or other suitable synthetic resins in suitable proportions. The kneaded homogenous mixture is charged under a specified technical process. While this operation is carried the total mass of mixture in the mould is kept in uniform hot condition to avoid manufacturing defects while pressing.
This furnace crucible is mostly used for melting non-ferrous precious metals such as brass, copper, nickel, chromium as well as their alloys. The silicon carbide furnace crucible is inspected for lamination, cracks, etc. and then placed in a kiln for firing at 1350-1400 degree celsius under reducing atmosphere to avoid oxidation of graphite and carbon. To create a reducing atmosphere, the silicon carbide graphite furnace crucibles are loaded into specific fireboxes tightly packed with reducing agents like coke/coal dust, sometimes graphite powder.
1.1.3. Clay graphite crucible
The main components of clay graphite furnace crucible are natural flake graphite and clay. Clay graphite furnace crucible contains 30% to 50% of graphite, the refractoriness of clay graphite crucible is similar to clay bricks, but thermal shock resistance and chemical corrosion resistance of clay graphite furnace crucible is significantly better than clay bricks. Clay graphite furnace crucibles are used in high temperature melting of iron, steel, copper alloys or melting of precious metals which can handle large batches of material.
Their thick walls can handle direct heat and open flame foundries. They are mostly used with gas or propane and medium/high heat furnaces and kilns. The clay graphite furnace crucible can withstand a temperature of 850 to 1600 degree celsius. The clay graphite also needs to be preheated or tempered at 300 degrees celsius for an hour before melting can be done with it. If tampering is not done and metals are melted directly, it can cause damages to the clay graphite furnace crucible.
The performance characteristics of the clay graphite furnace crucible are; controlled electrical resistivity, good thermal conductivity, good resistance to chemical corrosion, high refractoriness and good oxidation to resistance.
In melting with a clay graphite furnace crucible, light metals should be charged first before heavier metals, the light metals serve as a cushion for the heavier materials.
1.2, Quartz Crucible
Quartz crucibles have many desirable properties including high chemical purity, high corrosion resistance, high melting point, extreme hardness, low coefficient of thermal expansion, excellent electrical insulation, good corrosion resistance to ensure product quality and reliability, etc.
Metals with very high melting points such as palladium and platinum are usually melted with the quartz crucible. Platinum has a melting temperature of 1768 degree celsius while palladium has a melting temperature of 1555 degree celsius. The best type of crucible that can melt and hold these high melting temperature metals is the quartz crucible simply because it can stand high and varied use. Quartz crucible can also be used in alloy steel smelting, and smelting of nonferrous metals and their alloys. Quartz crucible can be used for special alloy refining.
1.3, Metal Crucible
Metal crucible may be in the form of steel, which can be used to melt metals whose temperature is less than 1500 degree celsius, because steel melts between 1500 to 1600 degree celsius.
Homemade steel crucibles can be used to melt metals such as aluminum and zinc, because these metals melt at a temperature well below the melting temperature of steel. However flaking (scaling) of a steel crucible interior surface is a drawback. This scale can contaminate the melt and slender the walls of crucible rather quickly. Coating of marcote-7 can be applied to the crucible to provide some level of protection between the steel and the metal being melted. Steel crucibles will work for starters in home foundry who don’t mind dealing with the scaling.
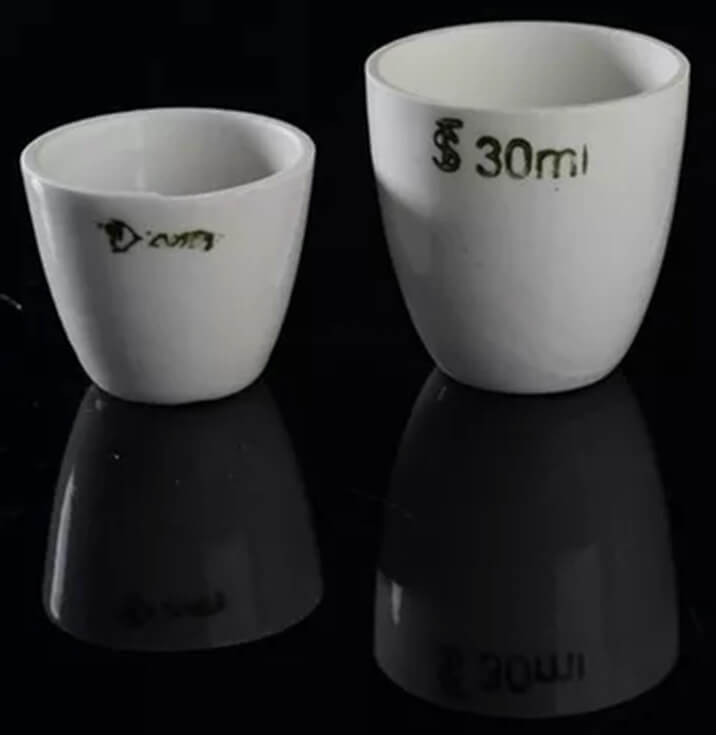
1.4, Porcelain Crucible
The term porcelain refers to a wide range of ceramic products that have been fired at high temperature to achieve vitreous or glassy qualities such as translucence and low porosity. Porcelain is a ceramic material made by heating ceramic raw materials, generally including clay in the form of kaolin, in a kiln to temperature between 1200 to 1400 degree celsius.
High thermal shock resistance of porcelain crucibles is attributed to the presence of mullite or cordierite structures. Hence, porcelain crucibles are classified as mullite crucibles. They are used in induction furnaces for melting glass and metals and in most cases, it is suggested for safe use up to 1700 degree celsius. The porcelain crucible is usually a cup-shaped container used in laboratories for heating purposes. The apparatus contain chemical compounds for heating at extremely high temperatures.
1.5, Which Material of Crucible is most Suitable for Precious metal Smelting Furnace
The different types of crucibles can be used in different melting applications based on the melting and smelting temperature. The modern furnace crucible is highly heterogeneous, graphite-based composite material, which relies on its composition and control of graphite structural alignment to achieve the desired performance.
Furnace crucible materials range from silicon carbide, graphite, clay graphite, porcelain, quartz, etc. They offer many different performance characteristics since each application presents a complex set of temperature, chemical and physical parameters which define the technical boundaries within which the furnace crucible has to be designed to operate. Before selecting the right crucible furnace for smelting, the following should be considered.
1.5.1. The melting and/or holding temperatures maintained
The metal, alloy or ore you want to melt or hold will determine the temperature range within which your furnace crucible. Crucibles should not be heated above their melting temperatures, this can lead to an irrevocable damage of the furnace crucible.
At the same time, operating below the furnace crucible’s lower temperature limit can also lead to problems during melting. Melting and holding practices should be taken into consideration before furnace crucible setup and use. If your smelting requires superheating, you need to take higher metal temperatures into account.
1.5.2. The temperature change rate the crucible will experience
The ability of a furnace crucible to handle the rate of temperature change is as important as its minimum and maximum temperature limits. Melting requires constant temperature changes and the furnace crucible you choose should be a to withstand the frequent furnace crucible temperature changes, i.e resistant to thermal shock. Some crucible types are much better at handling rapid temperature change than other types.
The high carbon content in a graphite furnace crucible contributes to its high thermal conductivity and non-wettability. When the graphite in the graphite furnace crucible forms a directionally oriented matrix, the crucible also provides high thermal shock resistance. This is critical to foundry operations where temperature changes by hundreds of degrees within a few seconds.
1.5.3. How the crucible is charged
If your furnace is always charged with molten metal then it does not require a furnace crucible that is designed to be highly resistant to physical damage. On the other hand, if your precious metal ingots or ores make up the bulk of your charge, and they are not carefully lowered into the furnace, through an automatic loading system, a crucible that is mechanically strong and able to withstand physical shock is highly recommended.
Crucibles that have high carbon content and a directionally oriented graphite structure are capable of such excellent impact resistance. A furnace crucible with a durable glaze is also recommended. Damage to the glaze from rough handling can lead to oxidation damage of the furnace crucible. Extruded aluminium ingots often have sharp edges that cut deeply into a furnace crucible’s body.
1.5.4. The fluxes or additions used
All furnace crucible models have some level of resistance to corrosion and chemical attack. Most of these fluxes and other metal treatments used in smelting and melting nonferrous metals are highly corrosive and require a furnace crucible that offers a high level of resistance to chemical attack.
This resistance is best impacted by both a consistently dense furnace crucible material structure and a durable protective glaze. For example, to separate gold from heavy material, the enriched pre-concentrate is placed in a furnace gold crucible with borax and baking powder or ammonium chloride and heated at a temperature of 1200 degree celsius.
This causes the oxidic materials such as limonite, ilmenite, etc to melt. In the solid liquid system which is created, liquid gold concentrates at the bottom of the crucible underneath tha slag. The melting temperature of gold is 1063 degree celsius.
If your smelting requires the use of corrosive metal treatments, a furnace crucible that offers protection the appropriate level of protection against these agents is needed.
1.5.5. Furnace power
Another factor that should be considered when planning and checking your crucible requirements based on your furnace’s specifications is power availability. In many locations, power for melting or holding might not be available at all times or might be absurdly expensive at certain times or at certain levels. If this is the case at your facility, it may be particularly important to select an energy efficient furnace crucible.
How to Choose a Graphite Crucible (Match Crucible to your Application)
There are different types of graphite furnace crucibles that are specific for every application. The following should be considered before choosing a furnace graphite crucible for your melting processes.
2.1, The Type of Furnace
2.1.1, Fuel-fired furnace
Fuel-fired furnace is powered by gas, oil, propane or coke. Each of these fuel types exposes the furnace crucible to the heat source and each provides a different level of heat to the furnace crucible.
Inga, oil and propane furnaces, the crucible must be able to withstand that effects of the burner flame at the bottom of the furnace and crucible must be tapered to allow the flame to circulate round the crucible from bottom to top. This allows even heating of the crucible.
The crucible material also must be able to resist oxidation damage from direct flame and accommodate the rate of thermal change the furnace crucible will encounter. Good thermal conductivity and even heating are important graphite crucible properties in transferring the heat from the interior of the furnace through the crucible to the metal charge.
Graphite furnace crucibles have high graphite content in the carbon binder offers high thermal conductivity for fast melting in gas-fired furnaces.
2.1.2, Electric resistance furnaces
Electric resistance furnaces provide an even and all-round heating to a furnace crucible and are ideally suited to precise temperature control in metal holding application. When compared to fuel-fired furnaces, they are slower in melting applications.
Crucibles with high graphite content in the carbon binder are often selected to provide high thermal conductivity for faster melting in this type of furnace. Crucibles designed for electric resistance furnaces are normally basin shaped and provide a uniform distance between the crucible and the furnace heating elements.
2.2.3, Induction furnace
Selecting a furnace crucible is often the most challenging. In some applications such as refining of precious metals, furnace crucibles designed to heat in the furnace crucible’s inductive fields are used to melt the charge. In other applications, furnace crucibles that allow the inductive field to pass through them and directly heats the metal charge are used.
The electrical characteristics of the graphite furnace crucible matches the operating frequency of the furnace and to the metal melting application. For some induction furnace designs such as the lower frequency induction furnaces require crucibles with high silicon-carbide content.
In other applications, high frequency induction furnaces require crucible with high clay content. Matching a crucible’s electrical resistivity to the induction furnace is key to preventing crucible overheating. Crucibles designed for induction furnaces are cylindrical, this is to provide a uniform distance between the crucible and the furnace coil.
2.2, The Capacity and Dimension of the Furnace
The capacity of a furnace refers to the amount and size of your melting, could be small, medium or large. There are different sizes of furnace crucibles that are suitable for every melting capacity (250g, 500g, 1kg,2kg, 4kg, 8kg, etc).
The dimension refers to the amount of space your furnace crucible will occupy inside the furnace. It will determine if your furnace crucible will come with spout and the size of the furnace crucible.
2.3, The Specific Alloy or Range of Alloys You Melt
Alloys are a combination of metals, the following metals are made of two or more alloys, steel, bronze, brass, aluminum, copper, etc. All melting temperatures of these alloys are less than graphite crucible melting temperature, which is 3600 degree celsius. Understanding the melting temperature of the alloys you melt will help to establish the maximum temperature the furnace crucible must support.
For instance, silicon carbide crucibles are used for melting copper based alloys in fuel-fired furnaces simply because these crucibles perform better due to high thermal shock resistance. In other types of furnaces, electric resistance furnaces and induction furnaces, crucibles are selected because of their high density. Less dense and more porous crucibles may cause erosion.
What are the Advantages of Superbmelt Furnace Crucibles
3.1, We Are the Factory
Superbmelt is an induction furnace graphite crucible manufacturer and furnace crucible supplier; that has been in the business of making high quality furnace crucibles for some years now. Our standard and quality products have distinguished us from the pack, this has however led to the approval and endorsement of quality certifications such as SGS, ISO etc.
We control all processes of furnace crucible production, from sourcing and analyzing raw materials to how the furnace crucibles are made to final usable products. Our equipment and brilliant service team work to ensure production of only high quality furnace crucibles.
3.1.1. How we Control Raw Materials
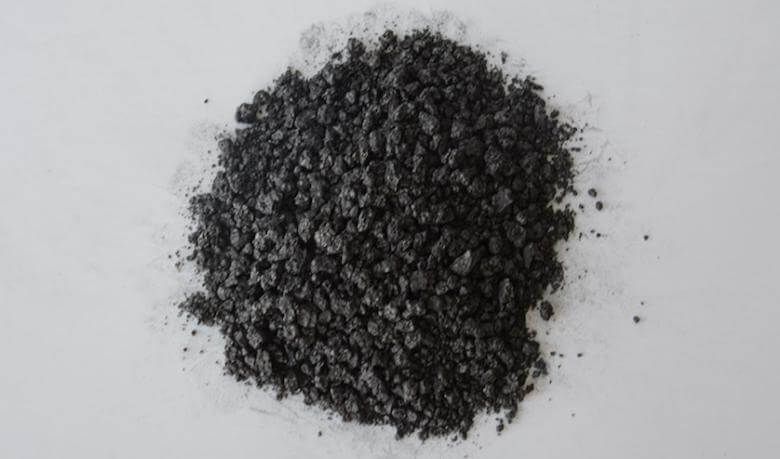
We produce our furnace crucibles from graphite made from processing petroleum coke and pitch coke. The graphite used in the manufacturing of crucibles go through a certain degree of processing with our sophisticated technology, that results in a product with a very homogenous and high density structure.
This contributes to our furnace crucible superior thermal conductivity over its entire operating temperature range, high mechanical strength and erosion resistance along with good thermal shock resistance. These properties translate into a durable and robust furnace crucible with excellent performance characteristics in higher temperature environments. The primary components of our graphite crucibles are:
Pitch coke (produced from coal tar that appears during coke production). Pitch coke is manufactured by coking the destructive distillation of coal tar pitch from high purity carbon residue. It has high content of carbon and low content of sulphur and ash. Pitch coke also has high thermal conductivity. It is a byproduct of coal gas manufacturing.
Petroleum coke (petcoke) is the gray-to-black solid carbonaceous residue left by the destructive distillation of petroleum residua. Petcoke is used in the production of graphite, smelting and chemical industries.
We produce graphite of various densities with these components. The level of density has an impact on the level of porosity of our gold crucibles, which implies that the higher the density of graphite, the lower the porosity of the crucible and the lower the density of the graphite, the higher the porosity of the crucible. Also, the higher the durability of the gold crucible, the higher the melting qualities; this gives the gold crucible a longer service life for vacuum utilization.
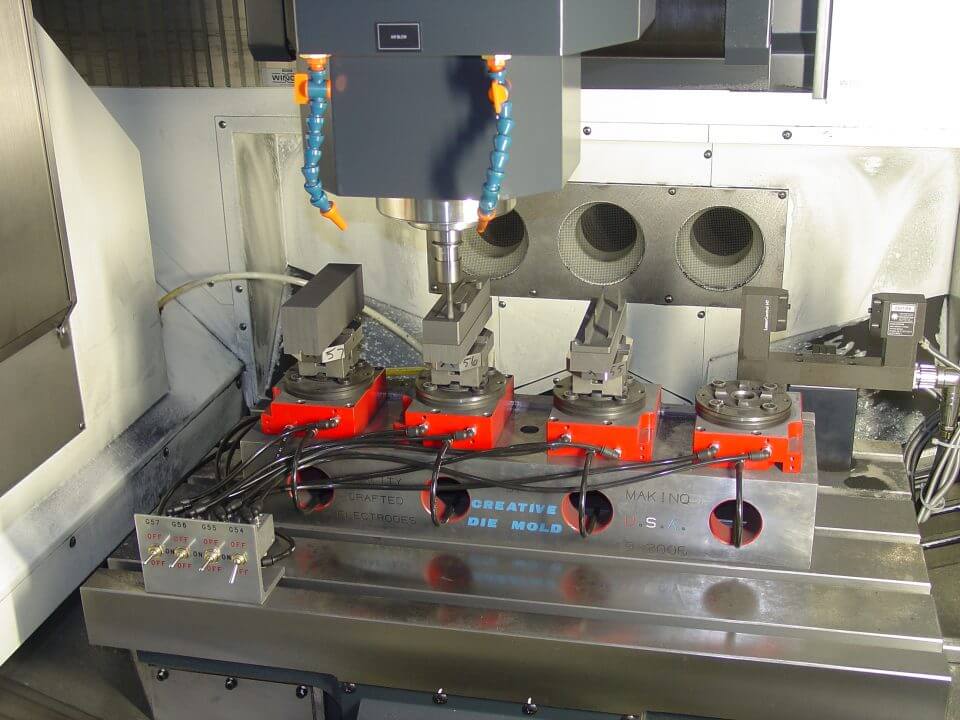
3.1.2. How we Process by CNC
Graphite furnace crucible materials are characterized by high purity, high strength, high density graphite material; through the high precision CNC machining equipment, graphite crucibles, graphite casting crucible, graphite oil groove, slide, drawing tablets, pull rod of mold graphite products.
The well laid CNC machining centre enables us to manufacture these precision crucibles using high grade graphite materials. Our highly skilled machinists combine all raw materials to allow the CNC to machine graphite to the most demanding specifications and exacting tolerances.
There are three different unique graphite processing levels for all Superbmelt furnace crucibles, they are; the moulded graphite process, isostatic pressed graphite process and medium coarse graphite process.
- Moulded graphite process
Moulded means it is cold pressed by molding. It is a type of graphite that is isostatically pressed. The resulting graphite material that has excellent properties uniformly distributed throughout the entire mass without having a grain direction.
Combine that with high density and small particle size, and the result is a highly engineered material, very strong, with good machinability, and capable of retaining very fine details. It is resistant to high temperatures in controlled environments, electro-conductive and has self lubricating properties.
- Isostatic pressed graphite process
The isostatic pressing technology is a super high pressure hydraulic equipment and its working principle is that products formed under the condition of equal pressure and high pressure in all directions and closed high-pressure containers. Properties of isotropic, structural balance, high conductivity, high purity, high strength, high density, high mechanical strength; superior thermal shock, high temperature resistance, resistance to oxidation and corrosion; fine-grained, low receptivity, and easy for precision machining.
The isostatic pressed graphite has the highest quality of all the three which comes with a higher price compared to the other two technologies. Isostatic graphite means that the raw material mixture is compressed into rectangular or round blocks.
In addition, isostatic graphite generally tends to have the smallest grain sizes of all artificial graphites. In this process, crucible void content is low and density is large, homogeneous and erosion resistance is strong.
- Medium coarse graphite process
The graphite particles are coarse this is as a result of the low compression resistance and bending resistance. The medium coarse graphite is used mostly for heat exchangers and heating elements. The medium coarse graphite is best used for frequently used crucibles and furnaces.
3.1.3. How we Carry Out the Testing
Supermelt crucible furnace manufacturing process also involves the process of testing for porosity, it is common to test small and crucible samples. A single pore or fissure of substantial size anywhere throughout the length of the crucible can cause cracking and render the entire piece unusable.
The method we employ in testing crucibles furnaces for the presence of undesirably large pores or fissures, this method comprises immersing the crucible in water, reducing the atmospheric pressure over the surface of the water to a point where bubbles are observed coming from the pores in the graphite surface and visually determining the existence of any pores which yield air bubbles of a diameter sufficient to indicate an undesirably large pore or fissure in the graphite crucible. The purpose of this testing is to ensure that we deliver top quality and long lasting furnace crucibles to all customers.
3.2, Graphite Crucibles Are Shipped Extremely Fast
When you purchase your furnace crucibles from Superbmelt, you enjoy swift delivery within three days. Your crucible orders are carefully packed to prevent damage or crack of your furnace crucibles and delivery is express through DHL or the United Postal Service (UPS).
3.3, ISO CE SGS Approved
Superbmelt has global and national certifications of product standards. Our crucible products have been inspected, tested, verified and certified. The SGS ( Société Générale de Surveillance) certification is in compliance with national and international standards, regulations and customer defined standards that our products have met.
Our furnace crucibles are CE (Conformitè Europëenne Mark) certified, which implies that they are quality enough to to be sold in European markets, i.e. meets all EU requirements of safety standards, fits its purpose and will not endanger lives and property.
Superbmelt furnace crucibles are also ISO (International Organization of Standardization) certified. The ISO certification certifies that our manufacturing process and service has all requirements of standardization and quality assurance.
3.4, Readily Available Service Team with 24 Hours Support
Superbmelt strong service professionals are always available to assist you with inquiries and proper guidance to your furnace crucible choice and use. We put our customers first and we ensure to meet your furnace crucible needs.
Conclusion
Buying high quality and long lasting furnace crucibles can be difficult especially when you are not aware of what crucibles are made of. We have been able to expose you to the different types of crucibles and the best choice of furnace crucibles you can make to enhance your melting.
Superbmelt furnace crucibles are enriched with features such as; high thermal conductivity, high thermal shock, excellence resistance to acidity and alkalinity, high heat resistance, corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, anti-adhesion.
These features give high melting quality, no loss of precious metal, no contamination of metal and no oxidation of metal after melting. Superbmelt furnace crucibles are pocket friendly and long lasting. We guarantee a seamless melting for your production.
FAQ Guide
What is a crucible furnace?
Crucible furnaces are one of the oldest and simplest types of melting furnace units used in the foundry. The furnaces use a refractory crucible which contains the metal charge. The charge is heated via conduction of heat through the walls of the crucible. The heating fuel is typically coke, oil, gas or electricity. Crucible melting is commonly used for small and large batches of medium and high melting point of metals and alloys are required. The capital outlay of these furnaces makes them attractive to small non-ferrous foundries. A crucible furnace is a simple and very old type of melting unit commonly used in foundry. The crucible furnace typically uses a refectory crucible which contains a metal charge. The actual crucible is a container that can withstand very high temperatures and is therefore used to melt materials such as metals, the crucible usually has a higher melting temperature than the metal being melted.
What can be used as a crucible?
Crucibles are basically made of materials that have high temperature resistance containers that come in various shapes and sizes (conical, beige, cylindrical, conical, etc). The most common materials used for furnace crucibles are graphite, silicon carbide, clay graphite, quartz, platinum, porcelain, inert metal etc. All these materials have various melting temperatures they can withstand during metal melting.
What is the best material for a crucible?
The best material for crucible is graphite. Graphite is an allotrope of carbon, which is a good electrical conductor. Being the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions, it is mined naturally to produce graphite furnace crucibles. The best material is graphite because they are the best electrical conductive material known to man, four times of steel, five times of copper, and hundred times of nonmetallic materials. They also give higher thermal conductivity than steel, iron and lead. The graphite material is highly resistant to acid, alkali and organic solvents.
What are the different types of crucibles?
The different types of crucibles are graphite crucibles, clay graphite crucibles, crucibles for melting gold, crucibles for melting silver, silicon carbide crucibles. The graphite furnace crucible is the best type of crucible because of its properties and affordability.
What needs to be checked before using a crucible?
Furnace crucible should be tempered before use. Heat the empty crucible at a low temperature for about 20 minutes. Then work the furnace crucible till red hot. Turn off the heat and leave the crucible to cool slowly. This process takes off any moisture in the crucible. Furnace crucibles should be properly checked for cracks prior to each application.
What temperature can a crucible withstand?
Crucible material must be able to withstand higher melting temperature than the metal. Graphite crucibles are temperature resistant and that is why they are mainly used in furnaces. It is essential that graphite crucible melting temperature is higher so it does not break when melting metals with very high temperature. The graphite crucible must have a much higher melting point than that of the metal being melted. Graphite temperature can range from 1600 and 2760 degree celsius.
Can you smelt brass in a steel crucible?
Brass has a relatively low melting point compared to iron, steel or gold. Brass melting point is between 900 and 940 degree celsius and its flow characteristics make it easy to cast. Steel crucibles are not recommended for temperatures above 700 degree celsius. A graphite crucible is ten times better for brass.
Why is it called the crucible?
The word “crucible” is from the medieval Latin word “crucibulum”. “Cruce” means pot, or jug and “ibulum” meaning censer.
Should you temper graphite crucibles?
Firstly, preheating of a crucible before use is important for reducing thermal stress on the crucible. A second reason to preheat a crucible is to ensure accurate measurements. If a crucible is weighed cold, or below room temperature, it is possible that moisture may become trapped in the material of the crucible. Heat an empty furnace crucible slowly at 200 degree celsius to eliminate any moisture, then heat on low power at 600 degree celsius. Heat on full power till bright red heat. Crucibles for melting application should continue to be heated on full power until the desired temperature is reached.
How do you warm up a crucible?
A crucible needs to be warmed up slowly and evenly to 600 degree celsius on low power. Subsequently, the full heat input rate should be utilized to achieve a uniform bright red condition over the whole crucible at which point the crucible should be charged immediately taking care to avoid packing metal tightly or bridging ingots across the crucible. Warming up a crucible before filling in metals is done for the following reasons: Preheating helps to reduce thermal stress; and to ensure accurate measurements. If a crucible is weighed cold or below room temperature, it is possible that moisture may be trapped in the material of the crucible. This moisture leads to variable amounts of excess weight.
How do you clean a crucible?
Step 1: Gently scrape as much residue left from the materials used in your experiment from the crucible. Step 2: Fill your ceramic crucible with fused potassium bicarbonate (solid form). You should have enough bicarbonate in the crucible to fill past the line of the remaining material from your experiments. If you need to fill the entire crucible, do so. Step 3: Place the crucible on a burner. Heat the crucible until the fused bicarbonate melts. Heat it until a layer of red potassium salt appears on the surface. Using a mixing rod, stir the melt a few times. The entire melting procedure should take about one minute. Step 4: Remove your crucible from the flame. Pour out the melt. Step 5: Rinse the crucible in hot water. Use a clean cloth to dry the surface. If your crucible is platinum, use alumina-impregnated nylon webbing to complete cleaning the surface. Let the crucible cool.
What are crucibles made of?
Furnace crucibles are often made of clay graphite, porcelain, platinum, inert metal, silicon, silicon carbide and graphite.
Why must crucibles be cooled before weighing?
Crucibles must be allowed to cool before weighing because the heat from the crucible warms the surrounding air which rises, then the air cools down and falls The rise and fall of surrounding air is called a convection current that gives unsteady reading that is rising and falling. Other reasons for allowing crucibles to cool before weighing is that a crucible is hot enough to transfer heat to the weighing balance, potentially damaging it but at least affecting measurement due to expansion of the balance components.
How do you use a crucible furnace?
A furnace crucible is very easy to use, before use, the crucible has to be preheated or tempered in a furnace before filling with cold metal. To maximize crucible reliability and service life, preheating instructions should be followed to the letter. This prevents thermal shock.
What is an induction furnace principle with crucible?
An induction furnace consists of a nonconductive crucible that is holding the charge of metal to be melted, the crucible is surrounded by a coil made of copper wire. A powerful alternating current flows through the wire. The coil creates a rapidly reversing magnetic field that penetrates the metal. The magnetic field induces eddy currents inside the metal by electromagnetic induction.
Can the same crucible melt all metals?
It is not advisable to use the same furnace crucible to melt different types of metals in a single crucible, this could lead to contamination of metal with other metals that would have been melted with fluxes and additives. Also mind not to melt copper or lead in the same crucible that you will use for steel. Lead will melt, go to bottom, seep through cladding and eat through the exterior wall if there is too much of it left and copper is oligoelement (i.e, a damaging element)that ruins steel. It is recommended that different furnace crucibles are used for different metals.

















 © Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited
© Copyright 2008-2021 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited