Portable Laser Welding Machine
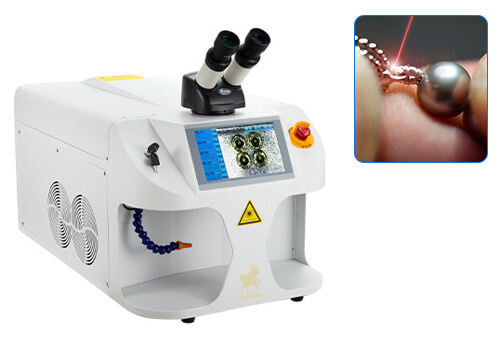

Superbmelt portable laser welding machine is used to weld noble metals together. Metals that can be welded with a handheld laser welding machine are; base metals, karat gold, sterling silver, palladium, platinum, etc. The handheld laser welding machine allows you to weld continuously while holding the precious metal pieces in your hand.
The camera and microscope system present in the small laser welding machine makes it easy for you to control and weld your metals. Superbmelt handheld laser welding machine for sale is used for jewellery repairs, medical, dental, electronic industries, antique stores, etc.
We are a laser welding machine manufacturer in China with ISO, CE, SGS certifications, we ensure all our machines are high quality, affordable and long-lasting.
We have a team of experts that always ensure to meet the demand of the market and customers’ expectations. Contact us today for your enquiries on the Superbmelt portable laser welding machine price.
| Model | SPB-150WB |
| Wavelength | 1064nm |
| Max output power | 150W |
| Max pulse energy | 80J |
| Pump source | Single lamp |
| Pulse width | 0.1-20ms |
| Pulse frequency | ≤50Hz |
| Aiming and positioning | Microscope + camera system |
| Application | Welding and repairing various precious metal trinkets |
| Host power consumption | ≤5KW |
| Electricity demand | AC220V±5%/50Hz |
| Cooling system | Water cooling + air cooling |
| Dimension | 660x385x435mm |
| Weight | 49kg |
- Superbmelt portable laser welding machine weld noble metal, karat gold, sterling silver, platinum, palladium, etc, at a wavelength of 1064nm.
- Superbmelt handheld laser welding machine is equipped with a microscope and a camera that allows you to aim and position metal parts during the welding process.
- The handheld laser welding machine guarantees a clean and smooth welding process. When you use a portable laser welding machine, there is no discolouration on the welded spot and surrounding area, compared with the soldering process.
- You can weld small parts, complicated, as well as dissimilar metals together, which would normally be impossible with other jewellery repair processes.
- The portable laser welding machine for sale requires low heat of ≤5kw. The low heat reduces the chances of distortion of metals after welding.
- Superbmelt portable laser welding machine has a water cooling system and air cooling system, to ensure maximum efficiency of welding and regulating heating temperature. This allows you to weld continuously.
- If you have a damaged antique or trinket, a Superbmelt handheld laser welding machine will effortlessly repair it for you.
- The handheld laser welding machine China has an imported ceramic condenser cavity that is both resistant to corrosion and high temperature. The imported ceramic condenser has a lifespan of 8 to 10 years, guaranteeing a long-lasting use of the entire portable laser welding machine.
- Superbmelt laser welding machine for sale is a compact size with a dimension of 660*385*435mm and a total weight of 49kg.
- Superbmelt small laser welding machine is suitable for use in jewelry repair and pawnshops, jewelry making, dental, medical, construction, electronics industries, etc.
- With the portable laser welding machine, there is no need for filler elements when welding your metals.
- The portable laser welding machine for sale guarantees excellent weld quality, clean and smooth welding process.
- The maximum output power and the maximum pulse energy for the portable laser welding machine are 150W and 80J respectively.
- The tightly controlled laser beam allows you to weld the smallest components.
- Superbmelt handheld laser welding machine is ergonomically designed for ease of use. You can conveniently place the portable laser welding machine on any surface proportional to your height.

2 years warranty
The warranty for our machine is one year longer than the warranty provided by other factories.

Strong service team
We will give response within 24 hours against your problem by our professional engineer.
Why SuperbMelt Portable Laser Welding Machine



Any Question About SuperbMelt Portable Laser Welding Machine
Portable Laser Welding Machine: Usage and Buying Guide
With the rapid advancement of laser welding technology, portable laser welding machines have gradually become a “must-have” across multiple industries due to their flexibility and efficiency. From precision work in small workshops to on-site maintenance in large factories, these machines are increasingly in demand. This guide will provide a comprehensive breakdown of portable laser welding machines—from target users, device types, core advantages, and key parameters to application scenarios—helping you accurately determine whether you need one and how to choose the model that best suits your needs.
Which users need a Portable Laser Welding Machine?
Portable laser welding machines are not “universal equipment”; their core value lies in “flexibly adapting to specific scenarios.” For the following types of users, choosing one can significantly improve efficiency and reduce costs:
1.1, Small jewelry/ornament workshops (individual practitioners / teams of ≤3 people)
- Core requirement: Perform precise welding on precious metals such as gold, silver, and platinum (e.g., chain links, pendant setting points), with welds that are hidden and oxidation-free, in a limited workspace (typically 10–20㎡ studios).
- Why a portable model is needed: Traditional desktop laser welding machines are large (occupying 1–2㎡) and difficult to place in small spaces. Portable devices, such as mini spot welders, weigh only 3–5 kg, can be placed on a corner of the workbench, or even moved as needed. They also deliver millimeter-level precision welding (weld diameter 0.1–0.3 mm), minimizing precious metal loss.
1.2, Hardware/kitchenware repair service providers (mobile repair teams / small shops)
- Core requirement: Provide on-site welding and repair for stainless steel kitchenware (e.g., sinks, stovetops) and hardware components (e.g., door/window hinges, railings), requiring the equipment to be carried to the site and weld positions to be flexible (e.g., high railings, narrow cabinet interiors).
- Why a portable model is needed: Industrial laser welding machines require fixed power and water-cooling systems, making them immobile. Portable devices, such as handheld fiber models, weigh 5–10 kg and come with lithium batteries (2–4 hours of runtime) or portable power sources, allowing quick setup on-site without relying on external utilities, while handling “non-flat welding” tasks (e.g., curved sink joints, vertical railing seams).
1.3, Electronic components/precision parts manufacturers (SMEs / R&D labs)
- Core requirement: Welding PCB pins, sensor terminals, and miniature mechanical parts (e.g., watch gears). Workpieces are small (typically 0.5–5 mm) and require flexible adjustment of welding positions on the production line or in a laboratory for sample development.
- Why a portable model is needed: Desktop machines are fixed to a specific workstation on the production line, and repositioning requires disassembly and reinstallation, which is time-consuming. Portable desktop models (weighing 8–15 kg) can be moved directly to any position on the production line or into the lab, supporting “multi-station switching” and “rapid sample iteration,” with welding precision up to ±0.01 mm, avoiding damage to delicate components.
1.4, Outdoor engineering/large equipment maintenance teams (e.g., steel structures, ship maintenance)
- Core requirement: Perform local weld repairs and reinforcements on outdoor steel structures (e.g., billboard frames, bridge railings) and large equipment (e.g., agricultural or construction machinery), in complex environments without fixed power or level ground.
- Why a portable model is needed: Traditional arc welding equipment is heavy (welders + cables over 20 kg), difficult to move outdoors, and welding precision is low (welds easily deform). Portable fiber laser welding machines (with wheeled stands or backpack designs) can be moved easily outdoors, powered by a gasoline generator, and provide a small heat-affected zone (0.5–2 mm), avoiding deformation of large components due to high-temperature welding.
1.5, DIY enthusiasts / makers (individual hobbyists / university maker spaces)
- Core requirement: Create metal handicrafts (e.g., brass jewelry, stainless steel models) or modify electronic devices. Budget is limited (usually under $5,000), and the user has no professional welding experience, requiring simple and safe operation.
- Why a portable model is needed: Industrial machines are expensive (over $10,000) and complex to operate, requiring professional training. Entry-level portable spot welders (priced $2,000–$4,000) are compact (laptop-sized), one-button start, and equipped with overload protection and anti-burn features. Beginners can quickly start using them, meeting DIY creation needs.
Common types of portable laser welding machines
Based on “size, power range, and core application,” portable laser welding machines can be mainly divided into three types. The suitability for different scenarios varies significantly, so it is essential to match the type precisely to your needs.
2.1, Mini jewelry laser spot welding machine (power: 150–300W)
Core Positioning: Fine spot welding for precious metals, representing “small but precise.”
Appearance & Size:
Dimensions: Approximately 30cm × 20cm × 15cm (similar to a microwave), weight 3–8kg, can be placed directly on a desktop without occupying extra space.
Operation Interface: Touchscreen + physical buttons, displays welding power, spot diameter, welding time, and other parameters; supports Chinese/English switching, easy for beginners.
Core Specifications:
Laser Type: Fiber laser (concentrated energy, suitable for precious metals).
Spot Diameter: 0.1–0.5mm (adjustable), can weld fine gold wire as small as 0.05mm.
Welding Thickness: Gold/Silver/Platinum 0.1–2mm, Copper 0.1–1.5mm.
Cooling Method: Air-cooled (no external water needed, suitable for desktop use).
Power Requirement: 220V household power (≤500W), no industrial electricity required.
Applicable Scenarios:
Jewelry: Chain link welding, pendant prong reinforcement, ring resizing and repair.
Precision Electronics: Watch movement component welding, micro sensor terminal welding.
Advantages & Disadvantages:
Advantages: Extremely high precision (no welding marks, no oxidation), minimal size, easy to operate, no professional training required.
Disadvantages: Low power, supports only spot welding (no continuous welding), not suitable for thick metals (>2mm).
Market Price: Entry-level (150W) $3,000–5,000; Professional version (300W, with microscope) $8,000–12,000.
2.2, Desktop laser welding machine (power: 300–1000W)
Core Positioning: Continuous welding for small to medium-sized workpieces, representing “desktop-level efficiency.”
Appearance & Size:
Dimensions: Approximately 60cm × 40cm × 30cm (similar to a washing machine), weight 15–30kg, equipped with caster wheels for easy movement within the workshop.
Structural Design: Comes with a small integrated worktable (40cm × 30cm) to secure workpieces; some models include simple fixtures (e.g., three-jaw chuck) for easy positioning.
Core Specifications:
Laser Type: Fiber laser (balances precision and efficiency).
Welding Mode: Spot welding / continuous welding (adjustable, continuous welding speed 0.5–3m/min).
Welding Thickness: Stainless steel 0.5–5mm, Aluminum 0.3–3mm, Copper 0.3–4mm.
Cooling Method: Water-cooled (built-in small water tank, 5–10L, lasts 4–8 hours per fill).
Power Requirement: 220V/380V optional (1–3kW), suitable for standard workshops.
Applicable Scenarios:
Hardware Processing: Welding small stainless steel parts (e.g., handles, hinges), continuous welding of brass accessories.
Electronics Manufacturing: Batch soldering of PCBs, welding terminals of small motors.
Laboratory: Prototype development of precision parts, metal material welding tests.
Advantages & Disadvantages:
Advantages: Supports continuous welding, 3–5 times more efficient than mini spot welders, fixed worktable ensures precise positioning, suitable for small-batch production.
Disadvantages: Requires periodic water refill (water-cooling system), heavier (requires 2 people to move), not suitable for outdoor scenarios without water source.
Market Price: Basic model (300W) $6,000–10,000; Advanced model (1000W, with automatic wire feeding) $15,000–25,000.
2.3, Micro Fiber Laser Welding Machine (Power 1000–2000W, primarily handheld)
Core Positioning: On-site welding for medium-to-thick metals, representing “mobile efficiency.”
Appearance and Dimensions:
Main unit size: approximately 50cm × 40cm × 25cm (similar to a suitcase), weight 20–40kg; some models come with handles or wheels.
Welding head: handheld design (weight 1–2kg), connected to the main unit via a fiber optic cable (length 3–5m) for long-distance operation.
Key Parameters:
Laser type: high-power fiber laser (high energy density, suitable for thick metals).
Welding mode: primarily continuous welding (point welding optional), welding speed 1–5 m/min.
Welding thickness: stainless steel 1–10mm, aluminum 1–8mm, copper 1–6mm.
Cooling method: water-cooled (built-in large-capacity water tank 10–20L, or external portable chiller).
Power requirement: 380V industrial power (3–5kW); some models support generator power (≥5kW required).
Applicable Scenarios:
On-site repair: stainless steel cookware repair, door/window railing welding, agricultural machinery parts repair.
Outdoor projects: steel structure sign welding, partial ship repair, bridge railing reinforcement.
Factory workshops: welding internal points of large equipment (e.g., machine tool cavities, pressure vessels).
Pros and Cons:
Pros: flexible handheld operation (can weld at heights and in tight spaces), high power (suitable for thick metals), supports outdoor work.
Cons: requires some operator experience (to avoid misaligned welds), handheld welding head can cause fatigue with long-term use, higher cost.
Market Price: Entry-level (1000W) $20,000–30,000; professional models (2000W with oscillating welding head) $35,000–50,000.
Why are portable devices so popular? Core advantages
Compared to traditional welding equipment (such as arc welders or desktop laser welding machines), the popularity of portable laser welding machines is no coincidence—their core advantages precisely address key pain points in the industry:
3.1, Extremely compact, suitable for “small spaces”
Space Requirement
- Pain Point (Traditional Equipment): Desktop laser welding machines require a fixed space (2–3㎡) with additional room for heat dissipation and operation. Small workshops (10–20㎡) struggle to accommodate them. Arc welding equipment, although smaller, still requires gas cylinders (argon tanks) and cables, taking up significant space.
- Portable Advantage: The smallest mini spot welding machines occupy only 0.01㎡ of desktop space (roughly the size of an A4 sheet). Even the largest micro handheld units have compact main units that fit in a corner, with the welding head extended via fiber optic cable. For example, in a 15㎡ jewelry workshop, you could fit 2 mini spot welders plus 1 workbench, improving space utilization by 50%.
3.2, Highly mobile, overcoming the “fixed workstation” limitation
Mobility
- Pain Point (Traditional Equipment): Most traditional equipment is fixed (desktop machines need fixed power and water supply, arc welding gas cylinders are cumbersome). Welding large workpieces (e.g., 3-meter steel structures) or performing on-site repairs requires disassembly and transport, which is labor-intensive (2–3 people, 2–4 hours).
- Portable Advantage: Mini units are hand-carriable (3–8kg), desktop models with wheels (15–30kg) can be moved by one person, and handheld units (20–40kg) can be transported in a vehicle (e.g., SUV trunk), with fiber-optic welding heads for flexible operation. For example, a hardware repair team can weld a stainless steel sink on-site with just one handheld unit and a portable power source, completing setup in 30 minutes and improving efficiency 3–4 times.
3.3, Low operating threshold, easy for beginners to learn quickly
Ease of Use
- Pain Point (Traditional Equipment): Arc welding requires professional training (3–6 months) to avoid burn-through or weak welds. Desktop laser welders, although precise, have complex parameters (laser power, focus, welding speed, 10+ settings) that are difficult for beginners.
Portable Advantage:
Simplified Operation: Mini spot welders have preset “jewelry welding modes,” requiring only selection of weld spot diameter (0.1/0.3/0.5mm) and one-button start. Desktop models provide scenario-based parameters (e.g., “hardware welding,” “electronics welding”) without manual adjustments.
Safety Design: Equipped with laser safety goggles, overload protection (auto shutdown for unstable voltage), and heat-resistant casing, making it safe for beginners.
Learning Curve: Mini units: 1–2 hours to proficiency; desktop: 1–2 days; handheld: 3–5 days (mainly practicing hand stability), significantly shorter than traditional equipment.
3.4, High welding precision, reducing “rework and material waste”
Precision and Material Efficiency
- Pain Point (Traditional Equipment): Arc welding has a large heat-affected zone (5–10mm), easily deforming workpieces (thin stainless steel sheets warp) with rough welds requiring post-grinding. Desktop laser welders, though precise, struggle with micro workpieces (e.g., 0.1mm gold wire), resulting in 5–8% precious metal loss.
Portable Advantage:
High Precision: Mini spot welders have a minimum weld spot of 0.1mm and heat-affected zone ≤0.3mm. No post-grinding is needed, and precious metal loss drops to 1–2% (e.g., 18K gold chains save $10–15 per meter).
Consistency: Desktop units with workbench clamps achieve ±0.01mm positioning accuracy. In batch welding (e.g., 100 identical hardware pieces), weld deviation ≤0.05mm, with a pass rate above 99%, avoiding rework.
3.5, No complex supporting equipment required, lowering “startup costs”
Setup and Operating Costs
- Pain Point (Traditional Equipment): Desktop laser welders require industrial power (380V), water cooling (external pipes), and exhaust systems, costing $5,000–10,000 for setup. Arc welding consumes electrodes and argon gas regularly, costing $1,000–2,000 per month.
Portable Advantage:
Simple Setup: Mini units need only 220V household power (≤500W) with air cooling; desktop units have built-in water tanks (no external water needed) and run on 220V; handheld units may require 380V but can use a 5kW generator ($2,000–3,000) without industrial power modification.
Lower Consumables: The main consumable is the protective lens (replaced every 3–6 months, $50–200). No electrodes or frequent argon gas use. Monthly consumable costs are $100–300, 70–80% lower than arc welding.
Key parameters of portable laser welding machines
When choosing a portable laser welding machine, higher specs are not always better—it’s about matching your needs. The following six key parameters directly determine whether the equipment can meet your usage scenarios and should be given close attention:
4.1, Laser power: determines “maximum weldable thickness”
Power
Core logic: Higher power allows welding thicker metals, but excessive power increases energy consumption and enlarges the device (reducing portability).
Parameter selection guide:
For precious metals (gold/silver/platinum ≤2mm) or electronic components (≤1mm): choose 150–300W (mini spot welder); too high power may burn through the workpiece.
For hardware parts (stainless steel/aluminum 0.5–5mm): choose 300–1000W (desktop type), balancing precision and efficiency.
For thick metals (stainless steel >5mm, aluminum >3mm) or outdoor maintenance: choose 1000–2000W (handheld type) to ensure strong welds.
Note: Some manufacturers indicate “peak power” (e.g., “300W peak”), while the actual average power may be only 200W. Confirm average power to avoid being misled.
4.2, Spot diameter / welding speed: determines “precision and efficiency”
Weld spot diameter & welding speed
Core logic: Smaller spot diameter → higher precision (for micro workpieces); faster welding speed → higher efficiency (for batch production). Balance according to your needs.
Parameter selection guide:
Jewelry/electronics (fine welding required): spot diameter 0.1–0.5mm, mainly spot welding; speed not critical.
Small-batch hardware production (balance precision & efficiency): spot diameter 0.5–1mm, continuous welding speed 1–3 m/min (e.g., weld 1m stainless steel part in 3–5 min).
Outdoor maintenance / large-scale production (efficiency priority): spot diameter 1–2mm, continuous welding speed 3–5 m/min to shorten operation time.
4.3, Laser type: determines “welding quality and compatible materials”
Laser type
Core logic: Different laser types have different energy density and wavelength, affecting suitable materials and weld quality.
Comparison & selection:
| Laser type | Energy density | Suitable materials | Weld quality | Typical scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber laser | High | Gold, silver, platinum, stainless steel, aluminum, copper | Small spot, no oxidation, high strength | Jewelry, hardware, electronics, outdoor maintenance |
| YAG laser | Medium | Stainless steel, thin copper | Slightly larger spot, prone to oxidation | Low-end electronics, DIY (being phased out) |
| CO2 laser | Low | Rarely used for metals | Poor effect, prone to deformation | Not recommended for metal welding |
Conclusion: Fiber laser is the preferred type—wide material compatibility and excellent weld quality; the mainstream choice for portable devices.
4.4, Cooling method: determines “flexibility of usage scenarios”
Cooling method
Core logic: Laser welding generates heat; cooling method affects whether external support (water, power) is needed.
Comparison & selection:
| Cooling type | Principle | Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air cooling | Fan dissipates heat | No water, small size | Weak cooling, supports ≤300W | Mini spot welder (jewelry, electronics) |
| Water cooling | Water circulation in tank | Strong cooling, supports 300–2000W | Needs refill every 4–8h, risk of leakage | Desktop & handheld (hardware, outdoor maintenance) |
Selection advice: For locations without water (outdoor or client sites), choose water-cooled devices with large built-in tanks (≥10L) to avoid frequent refills. For desktop use, air-cooling (low power) or small tank water-cooling (high power) is fine.
4.5, Power requirements: determines “whether it can be used in the target environment”
Power supply requirements
Core logic: Different power levels require different voltage and current; ensure your site can meet the requirement.
Comparison & selection:
| Device type | Power range | Power requirement | Suitable scenarios | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mini | 150–300W | 220V household (≤500W) | Home studio, small workshop | Plug into regular socket, no electrical modification needed |
| Desktop | 300–1000W | 220V/380V optional (1–3kW) | Factory floor, lab | 220V requires ≥10A socket, avoid tripping |
| Handheld | 1000–2000W | 380V industrial (3–5kW) or ≥5kW generator | Outdoor projects, on-site repair | Generator should be pure sine wave; 220V may overload at full power |
Tip: Some handheld models claim “220V compatible,” but 2000W devices at 220V draw 9A; regular sockets may not support continuous use. Prefer 380V models or dedicated sockets.
4.6, Device weight and dimensions: determines “ease of mobility”
Portability (weight & size)
Core logic: Lighter & smaller → easier mobility; balance with power (higher power often means heavier).
Selection guide:
Frequent hand-carry (e.g., jewelers taking to exhibitions): mini type ≤8kg (3–5kg), size ≤30×20×15cm.
Push within workshop (A station → B station): desktop type 15–30kg with caster wheels, size ≤60×40×30cm.
Vehicle transport / outdoor use (maintenance teams traveling across regions): handheld main unit ≤40kg (fits SUV trunk), welding head ≤2kg (avoid hand fatigue).
Common application scenarios of portable laser welding machines
The application scenarios of portable laser welding machines essentially reflect a precise match between their advantages and the demands of specific use cases. Here are five typical scenarios with concrete applications, helping you clearly understand the value of the equipment:
5.1, Jewelry processing: millimeter-level precise welding, reduces precious metal loss
1. Jewelry and Precious Metals
Typical Workpieces: 18K gold chains, platinum pendants, silver rings resizing, diamond prong reinforcement.
Equipment Choice: Mini jewelry laser spot welder (150-300W, weld spot diameter 0.1-0.5mm).
Operation Process:
Secure the workpiece on the device’s fixture (ring in circular clamp, chain on positioning pins).
Observe the welding point through a microscope (some high-end models have HD cameras connected to a screen).
Select “Precious Metal Welding Mode,” set weld spot diameter (e.g., 0.3mm for chain links) and welding time (0.1-0.5 sec).
Press foot switch or touchscreen to complete the weld; no post-polishing needed (hidden welds, no oxidation).
Value: Traditional gas welding results in 5-8% material loss and blackened welds. Mini laser spot welders reduce loss to 1-2%, saving $2,000–$3,000 per 100 meters of chain, while doubling efficiency (50-80 welds/hour).
5.2, Hardware parts production: fast small-batch welding, adaptable to multiple types
2. Hardware and Metal Accessories
Typical Workpieces: Stainless steel handles, brass hinges, aluminum kitchen accessories, iron decorations.
Equipment Choice: Desktop laser welding machine (300-1000W, supports continuous welding).
Operation Process:
Install specialized clamps according to workpiece shape (V-clamp for handles, flat clamp for hinges).
Select “Stainless Steel” or “Brass” welding mode, set welding speed (e.g., 1.5m/min) and laser power (e.g., 500W).
Start welding; move the workpiece or let the machine auto-feed to complete continuous welds (e.g., a 10cm handle seam in 4 sec).
Post-weld, simply wipe; no visible weld marks.
Value: Small hardware shops (5-10 workers) using traditional arc welding require 1 skilled welder ($4,000–$6,000/month) and multiple setups for different materials. Desktop laser welding allows 1 operator to weld stainless steel, brass, and aluminum with quick parameter adjustments (<5 min), cutting labor cost by 50% and equipment cost by 30%.
5.3, Electronic component welding: precise and non-damaging, protects sensitive parts
3. Electronics and Precision Components
Typical Workpieces: PCB pins, sensor terminals, micro motor coils, watch movement parts.
Equipment Choice: Mini spot welder (200-300W with micro-focus lens) or desktop type (300-500W with precision worktable).
Operation Process:
Place electronic components on an anti-static worktable, secure with tweezers (e.g., 0.3mm PCB pin).
Adjust focus to ensure laser targets the weld spot (≤0.01mm error).
Set low power (200W) and short weld time (0.05-0.1 sec) to avoid heat damage.
Perform single spot welds or short continuous welds; test conductivity with a multimeter (≥99.5% pass rate).
Value: Traditional soldering often results in weak joints (85-90% pass rate) and can damage chips. Portable laser welders achieve ≥99.5% pass rate, no defects, ideal for small-batch R&D (100-500 samples/month) or repairs (e.g., mobile motherboard pins).
5.4, On-site repair services: rapid response on-site without customer cooperation
4. On-site Repairs of Metal Products
Typical Workpieces: Stainless steel sink leaks, door/window rail breaks, farm machinery wear parts, commercial kitchen seam cracks.
Equipment Choice: Micro fiber laser welding machine (1000-2000W, handheld, with portable power supply).
Operation Process:
Repair team brings equipment (main unit + welding head + portable generator) to the site; setup completed in 10 minutes.
Adjust power (1000-1500W) and welding mode according to material thickness (sink 1.2mm, rail 3mm).
Wear safety goggles; hold welding head on the weld point, complete in 5-10 seconds.
Light sanding if needed; clean site (minimal smoke or debris).
Value: Traditional repair requires transporting large parts (cost $500-1,000, 3-5 days). Portable welding allows on-site repair, service fee $1,000-2,000, cost $100-200, greatly improving profit and customer satisfaction.
5.5, Outdoor engineering and large equipment maintenance: adaptable to complex environments, reduces downtime losses
5. Outdoor and Large-scale Engineering
Typical Workpieces: Steel billboard frames, bridge railings, ship deck partial welds, hydraulic pipe interfaces of construction machinery.
Equipment Choice: Handheld micro fiber laser welder (1500-2000W, wind/dust resistant, with large-capacity water tank).
Operation Process:
Transport equipment to the site (main unit via forklift, welding head by hand), connect to gasoline generator (≥5kW).
Clean weld area, fix workpiece with clamps to prevent movement.
Select “Outdoor Welding” mode (device auto-adjusts laser power for wind); perform welding (e.g., 20cm railing break in 8 sec).
Inspect welds (hammer test for strength), complete maintenance.
Value: Traditional arc welding requires scaffolding ($10,000-20,000) and lower precision. Portable laser welding avoids scaffolding, offers high precision (small heat-affected zone, no structural compromise), reduces maintenance cost by 60-70%, and shortens downtime from 3-5 days to 1-2 days, saving $10,000-20,000.



 © Copyright 2008-2026 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited
© Copyright 2008-2026 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited