Laser Welding Machine Manufacturer
Top Manufacturer in China
- Jewelry Industry: Used for jewelry repair, custom jewelry making, and gemstone setting, ensuring precision welding and material integrity.
- Precision Manufacturing: Suitable for welding small components and thin metal sheets, commonly used in electronics and medical devices.
- Electronics Industry: Used for welding battery enclosures and connecting electronic components.
- Medical Devices: Used for high-precision welding of medical device parts.
20/30/50w laser engraving machine manufacturer
SuperbMelt, a leading Laser Welding Machine manufacturer in China, offers welding machines with power options of 80W, 150W, 200W, and more. SuperbMelt focuses on providing innovative laser welding technology to deliver fine welding solutions for jewelers and other manufacturers, helping you improve the quality and efficiency of your product processing.
In the jewelry industry, precision welding technology is crucial. SuperbMelt, with its high precision, stability, and efficiency, provides excellent welding solutions for jewelry manufacturers worldwide. Whether you need to repair fine jewelry or create complex custom pieces, SuperbMelt’s equipment helps you achieve the best results.
Our equipment has been successfully applied by jewelers and manufacturers around the world. Many customers have reported a 30% increase in production efficiency and significant improvements in welding quality, especially when handling precious metals and gemstone settings, with results that are truly unmatched.
Jewelry Laser Welding Machine List

80W Mini Laser Welding Machine
The 80w welding machine has a small and compact design, making it ideal for small jewelers, whether you want to get started in the jewelry business or want to increase your repair business in your jewelry store, you can choose this model.
This is definitely the best choice for first-time users, smaller jewelry studios and repair shops.
It is very budget-friendly, and the mini model can also save a fortune in transportation. At the same time, it is convenient to use and does not occupy space cost.
The air cooling system is adopted, when the temperature rises, it will automatically turn on, which ensures the efficiency of the jewelry welding machine.The machine is very small, easy to use, and does not take up space.
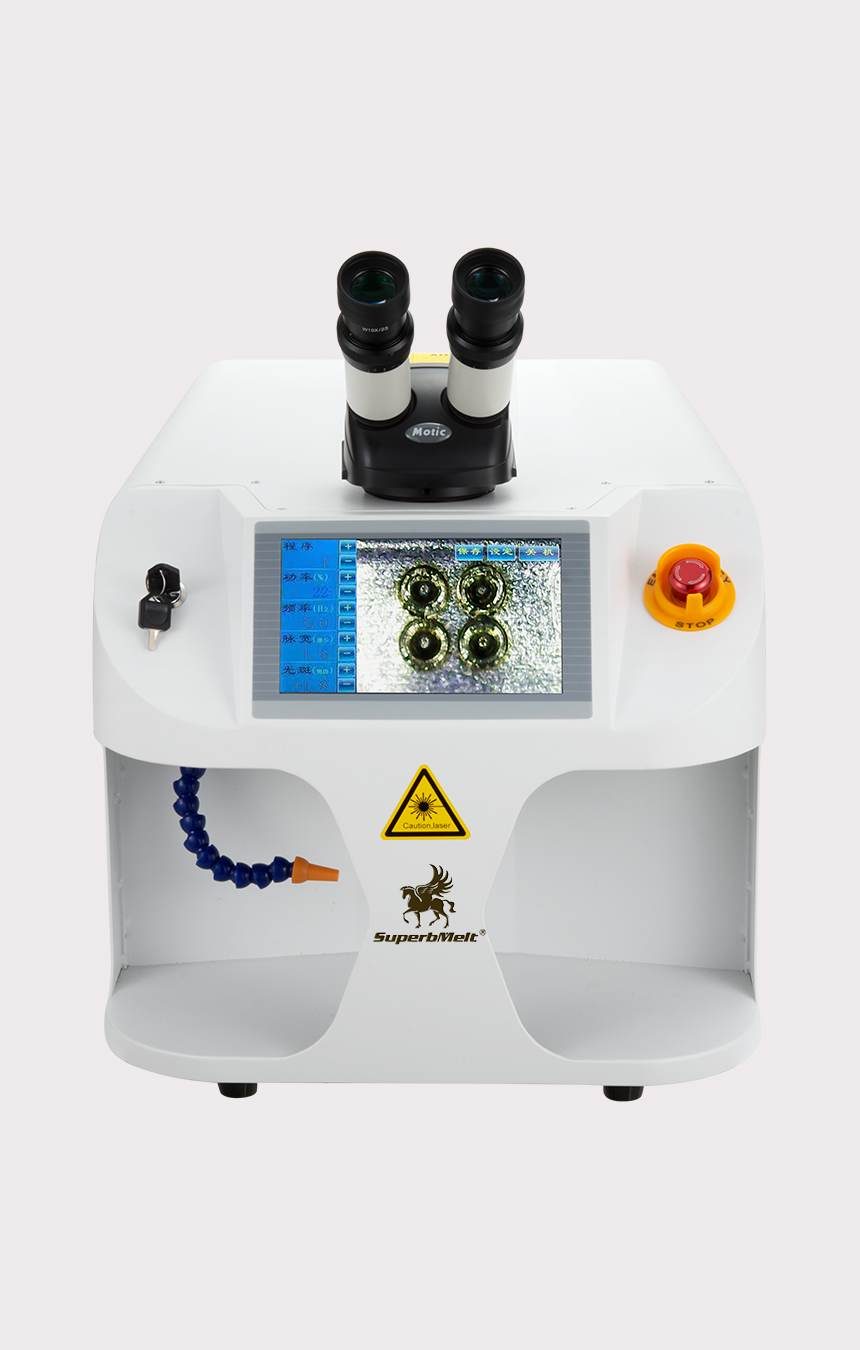
150W Mini Laser Welding Machine
SuperbMelt 150W welding machine is a desktop design, suitable for high-quality jewelry factory, small jewelry factories, and precision hardware laboratories.
Small in size and does not take up work space. The machine can customize the language to make it easier for customers everywhere to operate.
Air cooling and water cooling are integrated, using high-speed rotating fans and stainless steel water tanks to effectively prevent water leakage.
Such a cooling system provides conditions for continuous work and increases productivity.
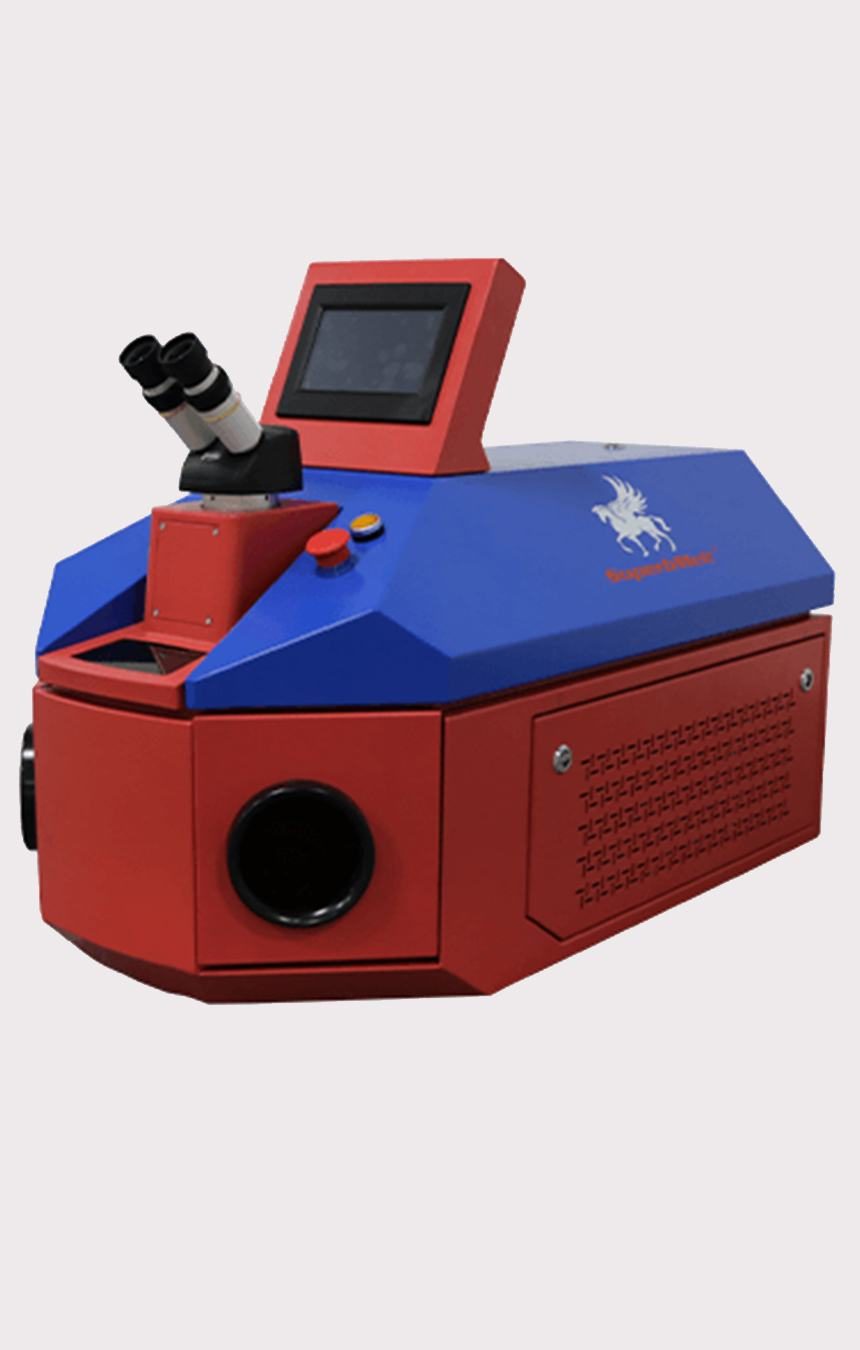

150W Jewelry Laser Welding Machine
The desktop jewelry welding machine is the best choice for jewelry industry applications with a high-quality laser source. It can be used to join and repair various metals.
At the same time, it is also widely used in denture processing, welding of battery covers, sensors, keyboards, etc.
It adopts non-contact welding method, because it is not directly exposed to the air like traditional welding machines, so there is no need to purchase additional safety glasses.
While meeting the requirements of cleanliness and environmental protection, the degree of automation is also very high.
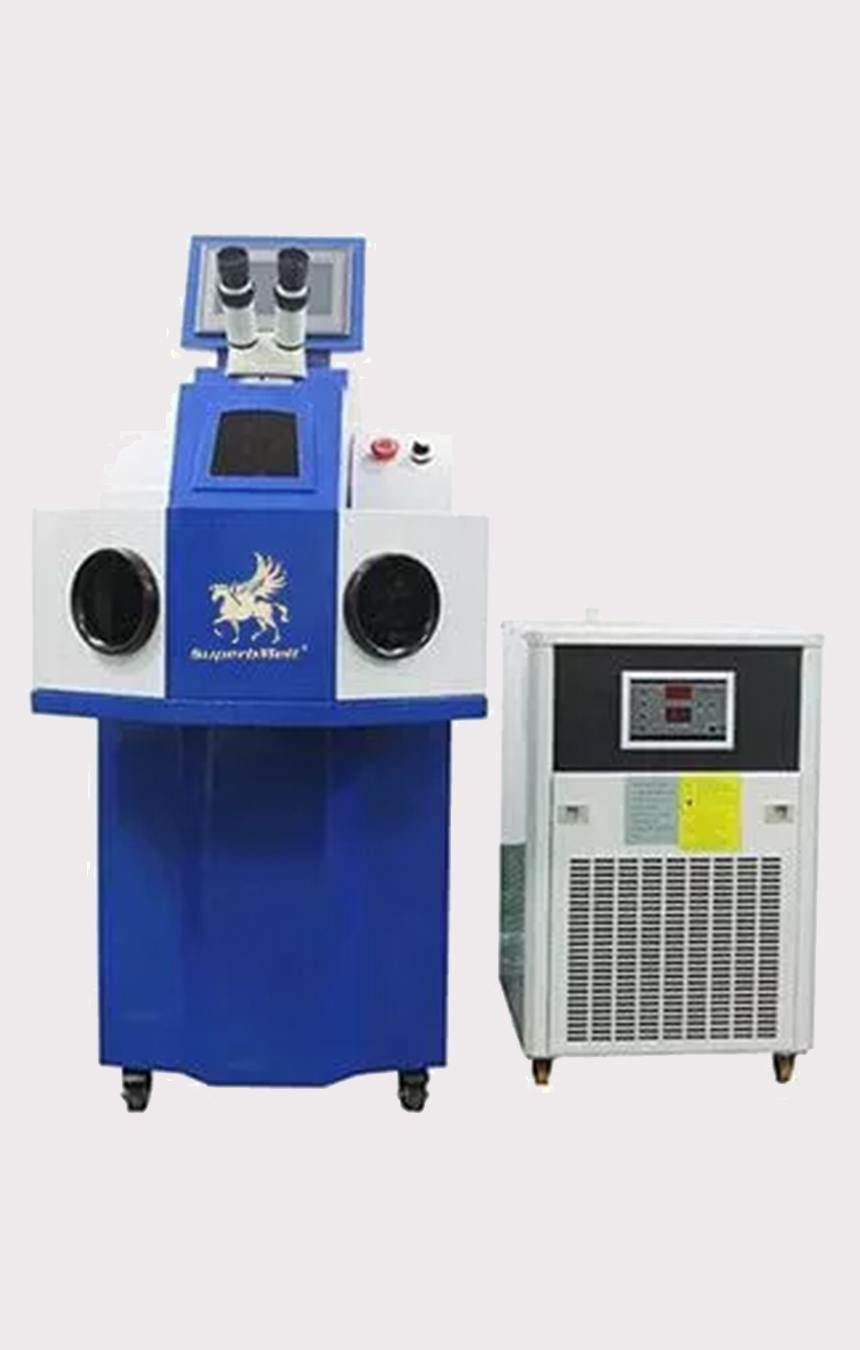

200W Automatic Laser Welding Machine
SuperbMelt automatic laser welder is a vertical design with an external water tank, which is suitable for large jewelry manufacturers. You could choose this model if you want to introduce an efficient jewelry repair machine for your jewelry factory, like bracelets, bangles, etc.
The machine works without noise and is environmentally friendly. High level of automation, simple buttons, use the LCD display, set the parameters, you can start working.
Equipped with a CCD monitorable system, which can make the welding effect more clear and intuitive.
This machine can be customized in wattage, 150 joules can reach a maximum pulse of 25ms and duration, and the spot diameter can reach the size of 0.3-1.5mm.
The size of the precision gets finer as the intensity increases. So it is well suited to serve more demanding jewelers, offering longer working hours and more power.
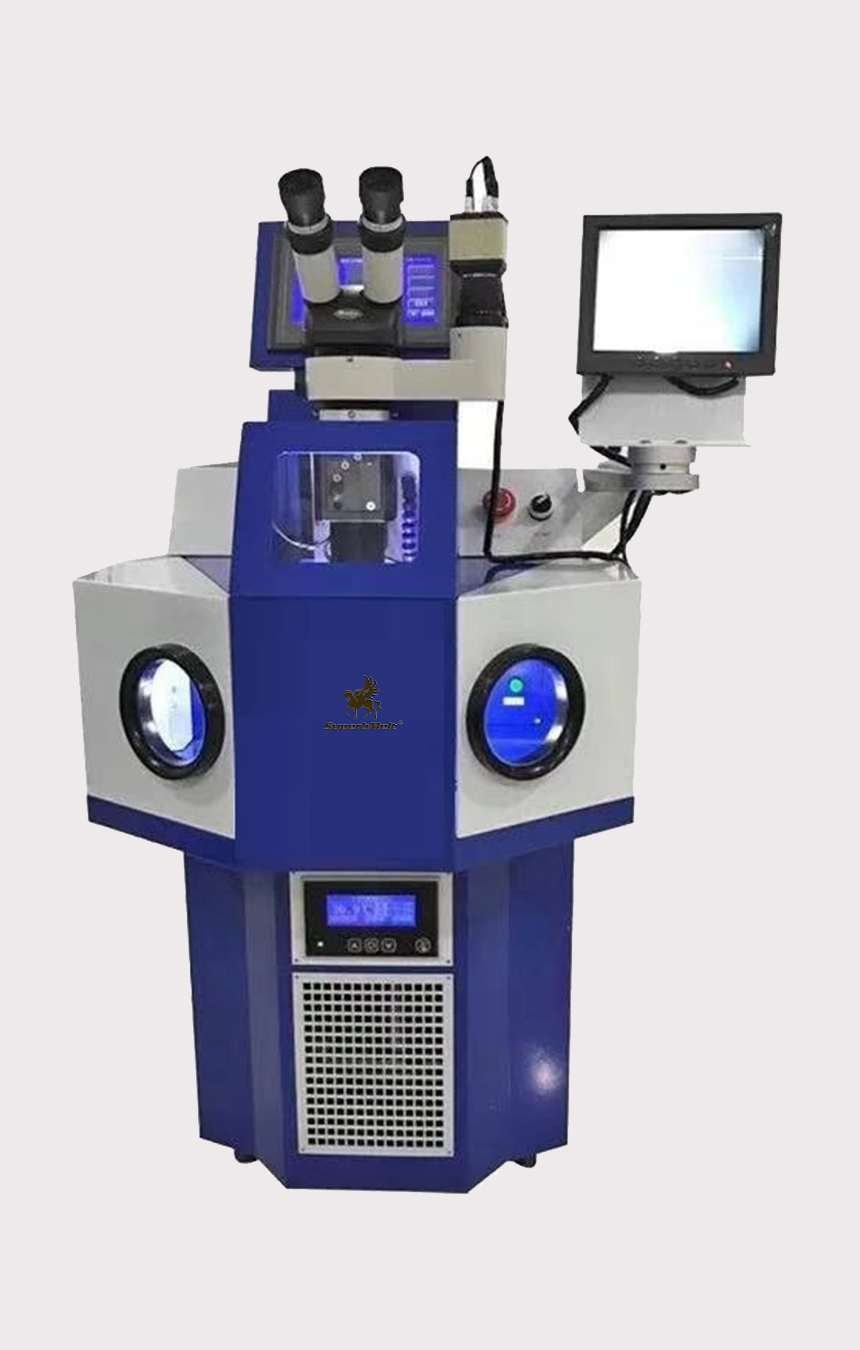

200W Laser Welding Machine with Internal Water Tank
This welding machine has an upgraded one-piece design with a built-in water tank.
Suitable for damaged jewelry of the same and different metal types, especially for welding small parts, so that it can provide perfect welding results in both the dental and jewelry industries.
With the use of the built-in microscope and camera system of the machine, precise aiming and positioning can be performed, so that the operator can see the status of the jewelry more clearly during welding, thereby reducing errors.
Models with internal and external water tanks like this are relatively large in size and are not suitable for small studios.
How to Smelt Platinum: The History of Platinum Smelting
How to Choose the Right Laser Welding Machine Manufacturer
Selecting the right laser welding machine manufacturer is critical for ensuring stable production, reliable weld quality, and long-term service support. Whether you’re in jewelry making, electronics, dental work, or precision metal processing, the quality of your machine depends heavily on the expertise and reliability of its maker. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Technical Expertise and R&D Strength
A reliable manufacturer should demonstrate strong research and development capabilities. Look for:
Years of experience in laser technology
In-house engineering teams
Patents or proprietary innovations
Customization capabilities based on your industry (e.g., precious metal welding vs. microelectronics)
2. Machine Quality and Performance
High-quality laser welders should offer:
Stable laser output with minimal fluctuation (±1%)
High positioning accuracy (≤0.01mm)
Advanced cooling systems for long-term operation
Durable build materials for machine longevity
3. Application Fit
Not all manufacturers specialize in your niche. Choose one with a track record in:
Jewelry manufacturing
Dental labs
Watch repair
Electronics and micro-welding
R&D laboratories
4. After-Sales Support and Training
Ensure the manufacturer provides:
Global shipping and installation guidance
Operator training (online or onsite)
Quick-response technical support
Spare parts availability and long-term maintenance plans
5. Customer Reviews and Case Studies
A reputable brand should be able to share:
Real user testimonials
Video demonstrations
Before-and-after welding samples
Reference clients in your industry
6. Certifications and Compliance
Check that the manufacturer and machine comply with:
ISO9001 quality standards
CE, FDA, or RoHS (depending on your region)
Safety standards for laser systems (Class 1 or Class 4)
Understanding the Power Options: 80W, 150W, 200W — What’s Right for Your Needs?
80W – For Delicate, Precision Tasks
Best For: Micro-welding, jewelry repair, fine prongs, chain links, watch components, dental welding
Advantages:
Minimal heat-affected zone
Excellent for fine, thin materials
Reduces the risk of warping or damaging gemstones or intricate parts
Use Case: A jeweler spot-welding a thin gold chain without affecting nearby stones
150W – The All-Purpose Choice
Best For: Medium-sized components, small jewelry production, mold repair, electronics
Advantages:
Versatile: balances power and precision
Supports both light and medium-thickness metals
Ideal for small-batch manufacturing
Use Case: A small workshop producing 50–100 silver rings per day with various thicknesses
200W – For Higher Throughput or Thicker Metals
Best For: Thick silver or gold parts, high-volume production, industrial jewelry workshops, tool/mold repairs
Advantages:
Higher penetration depth
Faster welding speed
Suitable for prolonged operation
Use Case: A factory welding large quantities of gold bangles or thick silver bars with consistent quality
Quick Selection Guide:
| Power Option | Best For | Metal Thickness | Use Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80W | Fine jewelry, dental, micro-parts | Thin (0.1–0.5mm) | Occasional/Precision |
| 150W | General jewelry making, mold repair | Medium (0.5–1.5mm) | Daily/Small batch |
| 200W | Production lines, thick pieces | Thick (1.5–3mm+) | High-volume use |
Core Technologies Behind a Professional Laser Welding Machine
Core Technologies Behind a Professional Laser Welding Machine
Understanding the internal technologies of a laser welding machine helps you appreciate what makes it an essential tool for fine metalworking. Here are the key components and systems that define a high-performance laser welder:
Laser Source (Nd:YAG or Fiber)
Nd:YAG (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet): Offers precise control and is commonly used in jewelry for spot welding.
Fiber Laser: Higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and better beam quality. Ideal for deeper, faster welding on a variety of metals.
Why it matters: Determines beam quality, energy efficiency, and suitability for fine or deep welds.
Beam Delivery System
Uses galvanometer scanners, optical lenses, or articulated arms to focus the beam precisely on the target.
Some systems include microscope-guided laser aiming for fine-detail work like prong welding or chain repair.
Benefit: Ensures pinpoint accuracy—critical for micro-welding.
Pulse Control & Power Modulation
Enables adjustment of pulse duration, frequency, and peak power.
Allows for welding metals of varying thickness and hardness without overheating or deformation.
Example: Lower pulse energy for thin chains, higher bursts for thick silver bars.
Cooling System (Water Cooling or Thermoelectric)
Prevents overheating of the laser cavity and optics.
Industrial models use closed-loop water chillers to maintain temperature stability.
Benefit: Extends machine life and ensures consistent welding quality.
Precision Optics and Aiming System
High-resolution microscopes, CCD cameras, or crosshair laser pointers assist with positioning.
Some machines offer digital screens with zoom capabilities for ergonomic operation.
Impact: Enables accurate targeting even on components smaller than 0.1mm.
User Interface & Smart Controls
Touchscreen interfaces with programmable welding parameters.
Memory settings allow users to save recipes for different materials (e.g., gold, platinum, silver).
Advantage: Simplifies operation and reduces the margin of error.
Gas Shielding System
Typically uses argon or nitrogen to protect the weld area from oxidation.
Delivers inert gas through a nozzle during welding.
Why it’s critical: Prevents discoloration, oxidation, and improves joint quality.
Summary Table
| Technology | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Source | Generates heat for melting metal | High precision, deep penetration |
| Beam Delivery | Directs laser beam | Focused energy, accurate targeting |
| Pulse Control | Adjusts laser output | Adapts to metal type/thickness |
| Cooling System | Prevents overheating | Stable long-term operation |
| Aiming Optics | Helps target welding points | Precise micro-welding |
| UI & Controls | Sets parameters & saves jobs | Operator-friendly |
| Gas Shielding | Prevents oxidation | Clean weld finish |
Precision Matters: Why SuperbMelt Leads in Fine Jewelry Welding
Precision Matters: Why SuperbMelt Leads in Fine Jewelry Welding
In the world of fine jewelry, every millimeter matters. Whether you’re welding delicate prongs on a diamond ring, repairing a fine gold chain, or setting intricate filigree patterns, precision isn’t optional—it’s essential. This is where SuperbMelt distinguishes itself as a global leader in jewelry laser welding technology.
Ultra-Fine Beam Control
SuperbMelt’s laser welding machines are equipped with high-resolution optics and pulse control systems, enabling precise targeting on components as small as 0.1 mm. This ensures clean, consistent welds without damaging surrounding stones or surfaces.
Optimized for Precious Metals
Gold, silver, platinum, and even mixed alloys require different welding parameters. SuperbMelt integrates material-specific welding presets and advanced power modulation to maintain weld integrity across all types of precious metals.
Clean Welds, Minimal Distortion
Using inert gas shielding and closed-loop water cooling, SuperbMelt machines reduce oxidation and thermal deformation—ensuring your pieces maintain structural and aesthetic perfection after welding.
Ergonomic Microscope Interface
Operators benefit from integrated microscopes with crosshair laser positioning or high-resolution CCD cameras. These features make detailed welds easier to perform and more reliable—even under demanding production conditions.
Designed for the Jewelry Industry
Unlike general-purpose welders, SuperbMelt’s systems are tailored for jewelers: from compact benchtop designs to multi-functional stations with engraving or polishing integration. This ensures a smoother workflow and faster turnaround without sacrificing quality.
Safety Features in SuperbMelt Laser Welders: What to Expect from a Leading Manufacturer
When working with high-precision laser equipment, especially in jewelry and metalworking industries, operator safety and machine reliability are top priorities. SuperbMelt, as a leading laser welding machine manufacturer, integrates comprehensive safety systems into all of its models to ensure a secure and user-friendly working environment.
Laser Shielding and Enclosed Working Area
SuperbMelt laser welders come with a fully enclosed laser chamber or protective hood that prevents direct exposure to the laser beam. High-transparency protective glass (typically with OD4+ rating or higher) allows clear visibility while blocking harmful laser radiation.
Foot Pedal Control with Emergency Stop
Every machine includes a hands-free foot switch to control the welding pulse, minimizing accidental laser firing. An emergency stop button is placed in an accessible position to allow immediate shutdown in the event of any abnormal operation.
Overheat and Power Surge Protection
Equipped with temperature sensors, cooling system alerts, and automatic shutdown in case of overheating or power surges, SuperbMelt machines actively protect both users and internal components from potential damage.
Water Cooling System Monitoring
For models using water-cooled systems, SuperbMelt includes low water level detectors and flow sensors, which automatically pause operations and issue alerts if cooling is insufficient—preventing overheating and laser tube failure.
Password-Protected Settings
To avoid unauthorized changes in machine settings, SuperbMelt allows for user permission levels or password-protected interfaces, which are ideal for training environments or multi-operator facilities.
Laser Interlock Systems
Many models feature safety interlock switches that immediately disable the laser if the working chamber is opened or not properly sealed, ensuring that the laser only operates in fully secured conditions.
Clear Safety Signage and Operator Guidance
All machines are shipped with clear safety labeling, training manuals, and proper use instructions. Optional training videos and user guidance sessions are available to help customers adopt safe practices from day one.
FAQ Guide of Laser Welding Machine Manufacturer
- 1. What are the advantages of laser welding over traditional welding methods?
- 2. What materials can be welded with a laser welding machine?
- 3. What power options are available for laser welding machines?
- 4. What maintenance is required for a laser welding machine?
- 5. What industries use laser welding machines?
- 6. How precise are laser welding machines?
- 7. What power supply is needed for a laser welding machine?
- 8. What is the difference between laser welding and laser cutting?
- 9. What is the minimum thickness of material that a laser welding machine can weld?
- 10. Is training required to operate a laser welding machine?
1. What are the advantages of laser welding over traditional welding methods?
1. High Precision and Accuracy
Laser welding offers superior precision, allowing for very fine welds, even on small or delicate parts. The focused laser beam creates minimal heat-affected zones (HAZ), which is crucial when working with thin or intricate materials like jewelry or electronic components.
2. Minimal Heat Distortion
Since laser welding uses highly concentrated energy in the form of a focused beam, it minimizes the heat spread to the surrounding area. This reduces the risk of warping, distortion, or material damage, especially when working with heat-sensitive materials.
3. Speed and Efficiency
Laser welding is much faster than traditional welding techniques, significantly increasing production speed and efficiency. The high energy density allows for quick processing, making it ideal for mass production or when time is a critical factor.
4. High-Quality Welds
Laser welding produces clean, precise, and strong welds with minimal spatter and no need for filler material in most cases. This results in smoother, more uniform welds that require less post-weld finishing.
5. No Need for Contact
Unlike traditional welding methods, which require direct contact between the welding tool and the workpiece, laser welding is non-contact. This reduces wear and tear on equipment and avoids contamination or damage to the workpiece.
6. Ability to Weld Small and Complex Parts
Laser welding excels in joining small, thin, or intricate parts that may be difficult to weld using traditional methods. It is especially beneficial in industries such as jewelry manufacturing, electronics, and medical device production, where small and precise welds are essential.
7. Less Post-Welding Work
Because laser welding results in clean and precise joints, there is less need for additional finishing, grinding, or cleaning after the welding process. This reduces labor costs and enhances overall productivity.
8. Versatility
Laser welding can be used to weld a wide variety of metals, including dissimilar materials (e.g., gold and silver, stainless steel and aluminum), making it versatile across different industries. Traditional welding may require more specialized processes or filler materials for different types of metal.
9. Reduced Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
The small heat-affected zone in laser welding means that the surrounding material is less likely to undergo unwanted changes, such as grain growth or structural weaknesses, ensuring the integrity of the welded part.
10. Automation Compatibility
Laser welding can easily be integrated into automated production lines, further enhancing efficiency and consistency in high-volume manufacturing settings. It’s suitable for automated systems that require fast, repeatable results.
11. Clean and Environmentally Friendly
Laser welding produces less smoke, fumes, and harmful emissions compared to traditional welding methods. It is a cleaner process, making it more environmentally friendly and safer for workers.
12. Remote Operation
Many laser welding systems can be controlled remotely, allowing for safer operations in hazardous environments and reducing the need for manual intervention.
2. What materials can be welded with a laser welding machine?
1. Precious Metals:
- Gold: Laser welding is commonly used for jewelry repair and creation, especially for high-end gold jewelry. It provides precise control without damaging the metal or gemstones.
- Silver: Silver is also frequently welded using lasers, ideal for creating intricate jewelry pieces or repairing silver components.
- Platinum: Platinum, due to its high melting point, requires a powerful laser welding machine. Laser welding offers precise control necessary for working with this precious metal.
- Palladium: Like platinum, palladium is a precious metal used in jewelry manufacturing and benefits from the precision and efficiency of laser welding.
2. Stainless Steel:
- Stainless steel is one of the most common materials welded using lasers. It’s widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics. Laser welding ensures strong, high-quality welds without excessive heat distortion.
3. Aluminum:
- Aluminum, known for its light weight and corrosion resistance, is often welded with lasers, particularly in automotive and aerospace industries. Laser welding of aluminum ensures minimal distortion and high weld quality.
4. Titanium:
- Titanium is commonly used in aerospace, medical, and automotive applications due to its strength and resistance to corrosion. Laser welding is an ideal choice for titanium as it provides the precision needed to handle the material’s high melting point.
5. Copper and Copper Alloys:
- Copper and its alloys, such as brass and bronze, can also be welded using laser technology. This is common in electrical and electronics applications, as copper is widely used for its conductivity.
6. High-Strength Steels:
- High-strength steels, such as tool steels and carbon steels, are often welded with lasers in industries like automotive and manufacturing, where durability and precision are crucial.
7. Carbon Steel:
- Laser welding is effective for carbon steel, commonly used in the automotive, construction, and manufacturing industries, where strong and durable welds are required.
8. Nickel Alloys:
- Laser welding can be used for welding nickel alloys, often found in aerospace, power generation, and chemical processing industries due to their high strength and resistance to heat.
9. Composites:
- Certain composite materials, such as fiber-reinforced plastics and metal matrix composites, can be welded with lasers, particularly in industries like automotive and aerospace.
10. Dissimilar Materials:
- One of the significant advantages of laser welding is its ability to join dissimilar materials. For example, a laser welding machine can join metals like aluminum and steel, which would be difficult to weld using traditional methods. This is useful in industries like automotive manufacturing, where different materials are used together.
11. Thin Metals and Sheets:
- Laser welding is particularly effective for thin metal sheets (as thin as 0.1mm) used in electronics, precision manufacturing, and medical devices. The minimal heat input ensures that thin parts are not distorted or damaged during welding.
12. Gold-Plated or Silver-Plated Metals:
- Laser welding can also be used to join plated metals without damaging the plating, which is particularly useful in jewelry and electronics.
13. Stainless Steel and Aluminum Combinations:
- Laser welding machines are ideal for welding dissimilar metals like stainless steel and aluminum, which are used together in many manufacturing applications, such as in automotive bodies.
3. What power options are available for laser welding machines?
Laser welding machines come in various power options, typically ranging from 80W to 200W, depending on the application and material thickness.
4. What maintenance is required for a laser welding machine?
1. Cleaning of Lenses and Mirrors
- Frequency: Regularly (weekly or after a set number of hours of operation).
- Why: Dust, soot, and other residues can accumulate on the lenses and mirrors, affecting the focus and efficiency of the laser. Cleaning ensures a clean, precise beam.
- How: Use a soft, lint-free cloth and special lens cleaning solution. Avoid using abrasive materials that could damage the optics.
2. Checking and Replacing the Laser Source
- Frequency: Periodically (as recommended by the manufacturer).
- Why: Over time, the laser source may degrade or wear out, reducing its power and efficiency. Replacing the laser tube or diode at the right time ensures consistent welding performance.
- How: Follow manufacturer instructions for inspection and replacement. Ensure the replacement part matches the machine’s specifications.
3. Cooling System Maintenance
- Frequency: Regularly (weekly or after a set number of hours of operation).
- Why: Laser welding machines often use water or a special cooling system to prevent overheating. Blocked or dirty cooling systems can cause the machine to overheat, affecting performance and potentially damaging internal components.
- How: Check coolant levels, inspect cooling lines for blockages or leaks, and clean or replace filters as necessary. Ensure the cooling fluid is free from contaminants.
4. Calibrating the Laser
- Frequency: Periodically (e.g., every 6-12 months or when performance drops).
- Why: Calibration ensures that the laser beam is focused correctly and aligns with the intended weld spot, maintaining precision and quality.
- How: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for alignment procedures. This may include adjusting the focus lens or optical system.
5. Inspecting and Lubricating Moving Parts
- Frequency: Regularly (monthly or as needed).
- Why: Moving parts, such as robotic arms or positioning stages, need to be properly lubricated to prevent wear and ensure smooth operation.
- How: Lubricate moving components with the appropriate type of grease or oil, based on the machine’s specifications.
6. Checking Electrical Components
- Frequency: Regularly (monthly or after significant usage).
- Why: Electrical issues, such as loose connections, faulty wiring, or power surges, can affect the machine’s performance or cause malfunctions.
- How: Inspect cables, power supplies, and control systems for wear, loose connections, or signs of damage. Replace faulty electrical components as needed.
7. Maintaining the Welding Gun or Nozzle
- Frequency: After every use or as needed.
- Why: The welding gun or nozzle can accumulate material buildup, which may obstruct the laser beam or affect weld quality.
- How: Clean the nozzle and welding gun thoroughly after use to remove any contaminants or buildup. Check for wear and replace nozzles or tips when they become damaged.
8. Monitor and Maintain the Control Software
- Frequency: As required (e.g., when software updates are available).
- Why: The software that controls the laser welding machine must be kept up to date to ensure smooth operation and the latest features.
- How: Regularly check for software updates or patches. Perform diagnostic checks to ensure the system is running optimally.
9. Inspecting the Exhaust and Ventilation Systems
- Frequency: Regularly (monthly).
- Why: Proper ventilation is essential for removing fumes and smoke generated during the welding process. Blocked exhaust systems can lead to safety hazards or overheating.
- How: Check exhaust filters and ducts for blockages or buildup. Clean or replace filters as necessary.
10. Periodic Performance Tests
- Frequency: Every few months or after significant changes in the machine’s operation.
- Why: Running performance tests helps identify any issues with the laser beam, power output, or overall welding quality.
- How: Conduct test welds on sample materials to assess the laser’s focus, power, and beam consistency.
11. Visual Inspection for Wear and Tear
- Frequency: Regularly (monthly).
- Why: Early detection of wear and tear can prevent expensive repairs or unexpected downtime.
- How: Perform visual inspections on the machine’s exterior, including joints, seals, and visible components, for any signs of damage, cracks, or wear.
5. What industries use laser welding machines?
Industries such as jewelry manufacturing, electronics, automotive, aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and metalworking all use laser welding machines for their precision and efficiency.
6. How precise are laser welding machines?
1. Focus Spot Size
- Precision: Laser welding machines can focus the laser beam to a spot size as small as 0.1 mm (100 microns) or even smaller, depending on the machine and the lens used. This high focusing ability allows the machine to create extremely fine welds, even in small or intricate areas.
- Impact: This precision is critical in industries where small, delicate components need to be joined without damaging surrounding areas, such as in jewelry welding or microelectronics.
2. Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
- Precision: Laser welding produces a very small heat-affected zone (HAZ), typically less than 1 mm in diameter. This means that the heat from the welding process is concentrated in a small area, minimizing the potential for distortion, warping, or heat damage to the surrounding material.
- Impact: A smaller HAZ is crucial in delicate applications where adjacent areas must remain unaffected by heat, such as when joining thin or heat-sensitive materials.
3. Laser Beam Control
- Precision: Laser welding machines provide highly controlled beam positioning and focus adjustments, allowing for precise placement of the weld. The beam can be adjusted with sub-millimeter accuracy.
- Impact: This ability to finely control the laser beam is beneficial for producing consistent, accurate welds in both manual and automated processes.
4. Reproducibility
- Precision: Laser welding machines are capable of high reproducibility, meaning that the same weld can be repeated multiple times with consistent results. This is due to their computer-controlled systems, which ensure that the laser’s parameters (such as power, pulse duration, and focus) are set and maintained to exact specifications.
- Impact: This feature is essential for mass production where consistent quality and precision are required across many identical pieces, such as in automotive manufacturing or mass jewelry production.
5. Ability to Weld Thin Materials
- Precision: Laser welding can effectively join very thin materials (even as thin as 0.1 mm), which is difficult with other welding methods. The machine’s precision ensures that it can deliver the exact amount of heat required to create a strong bond without causing damage to the thin material.
- Impact: This is especially beneficial in industries like medical device manufacturing, where precision and the ability to work with small, thin parts are critical.
6. Minimal Post-Weld Processing
- Precision: Due to the accuracy of the laser, laser welding often requires minimal post-weld processing, such as cleaning or smoothing. The welds are typically smooth and require little to no rework, reducing the overall processing time.
- Impact: This makes the process not only precise but also efficient, reducing labor and improving productivity in precision welding applications.
7. Micro-welding Capability
- Precision: Laser welding machines are ideal for micro-welding applications, where the precision of the weld needs to be controlled down to the micrometer level.
- Impact: This precision is vital in the electronics industry, for instance, where very small components must be welded with high accuracy, or in jewelry where fine details and intricate patterns are often involved.
8. Automated Precision
- Precision: Many laser welding machines come with automated systems that enhance precision by ensuring repeatability and minimizing human error. CNC (computer numerical control) systems are used to guide the laser and workpiece, allowing for precise and consistent welding along complex paths or patterns.
- Impact: Automated systems make it possible to weld at very high precision in mass production environments, ensuring that each weld is identical, which is crucial for applications such as medical implants and consumer electronics.
7. What power supply is needed for a laser welding machine?
Laser welding machines typically require a high-voltage power supply to operate, which varies depending on the welding machine’s specifications. Commonly, they require a 3-phase power supply with voltage ranging from 220V to 480V, depending on the machine’s laser power and application.
8. What is the difference between laser welding and laser cutting?
Laser welding uses a focused laser beam to melt and fuse materials together, creating a strong bond between them. Laser cutting, on the other hand, uses a laser beam to slice through materials to create specific shapes or designs. While both processes use lasers, the goals are different: welding joins materials, and cutting separates them.
9. What is the minimum thickness of material that a laser welding machine can weld?
Laser welding machines can weld materials as thin as 0.1 mm (100 microns), making them ideal for micro-welding applications. The exact thickness will depend on the laser power and material being used, but in general, laser welding excels in working with thin and delicate materials.
10. Is training required to operate a laser welding machine?
Yes, while some laser welding machines are designed for user-friendly operation, training is highly recommended to ensure the operator is familiar with the machine’s features, safety protocols, and best practices. Proper training helps prevent mistakes, reduces downtime, and ensures consistent high-quality welds.

 © Copyright 2008-2026 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited
© Copyright 2008-2026 Superb Electromachinery Co., Limited